Pipe Flange: The Ultimate Buying Guide In 2023
Pipe flanges are crucial components in piping systems, providing a method to connect and disconnect pipes or equipment, facilitate fluid flow, and create a secure seal. Choosing the right pipe flange requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and safety. This ultimate buying guide for pipe flanges in 2023 will provide you with the necessary information to make an informed purchasing decision.
1. What is a flange?

A flange is a mechanical device that is used to connect or join two pipes or components together. It is a flat or raised rim, typically made of metal, that is attached to the end of a pipe or equipment. Flanges provide a solid and secure connection, ensuring that the joint is stable and leak-proof. They also allow for easy disassembly and maintenance of the connected components. Flanges come in different shapes and types, and they serve to align, seal, and strengthen the joint between pipes or equipment in various industries.
2. What are the uses of flanges?
Flanges serve several important functions in various industrial applications. Here are some common uses of flanges:

- Connection and Joining: Flanges are primarily used to connect pipes, valves, fittings, and other equipment in a piping system. They provide a means of joining two components together securely and allow for easy disassembly when required. Flanges provide a leak-tight seal, ensuring the integrity and safety of the system.
- Pressure Containment: Flanges play a crucial role in containing fluid pressures within a piping system. The flange, along with appropriate gaskets and fasteners, creates a sealed connection that can withstand the pressure exerted by the flowing fluid. The pressure rating of the flange determines its ability to handle different levels of internal pressure.
- Flexibility and Alignment: Flanges allow for flexibility in the layout and alignment of piping systems. They provide a connection point where pipes can be easily joined or disassembled, allowing for modifications, repairs, and changes in system configuration. Flanges also help align and support pipe connections, ensuring proper alignment and stability.
- Accessibility: Flanges provide access points in piping systems for inspection, maintenance, and cleaning purposes. By loosening the bolts or studs that secure the flange connection, operators can gain access to the internals of the system, facilitating repairs, inspections, or cleaning of the pipes and components.
- Versatility: Flanges are available in a wide range of materials and dimensions to suit different applications and operating conditions. They can be manufactured from materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and more, enabling compatibility with various fluids, chemicals, and gases.
- Industry-specific Applications: Flanges find applications in various industries, including oil and gas, petrochemicals, power generation, water treatment, HVAC, pharmaceuticals, and many more. Different types of flanges, such as welding neck, slip-on, threaded, socket weld, and blind flanges, are used based on the specific requirements of the industry and the reliability needed for the application.
It’s important to note that the exact use of a flange may vary depending on the specific application and industry requirements. Flanges are crucial components in piping systems, providing secure connections, pressure containment, and accessibility for maintenance and modifications.
3. What are the benefits of using flanges?
The use of flanges offers several benefits in industrial applications. Here are some advantages of using flanges in piping systems:

- Secure Connection: Flanges provide a secure and reliable connection between pipes, valves, fittings, and other equipment. The bolted connection with gaskets ensures a leak-tight seal, minimizing the risk of fluid leakage or loss, which is crucial for maintaining system integrity and preventing environmental contamination.
- Versatility and Adaptability: Flanges are available in a wide range of sizes, materials, and designs, making them highly versatile and adaptable to different system requirements. They can be easily matched with pipes of varying dimensions, allowing for flexibility in system layout and configuration.
- Easy Assembly and Disassembly: Flanges facilitate easier and quicker assembly and disassembly of piping systems. With the use of bolts or studs, flanges can be securely connected or disconnected, providing convenient access for maintenance, repairs, or modifications. This ease of disassembly also enables faster pipeline inspections and cleaning.
- Enhanced System Integrity: Flanges help maintain the integrity of the piping system by providing a strong and durable connection. The sealing capability of flanges ensures that there is no leakage or seepage of fluids, minimizing the risk of system failures, accidents, or environmental hazards.
- Pressure Containment: Flanges are designed to withstand the pressure exerted by the flowing fluids within the piping system. The pressure rating of flanges is determined based on their construction and material, ensuring they can handle the specific pressure requirements of the application.
- Flexibility for Thermal Expansion: Piping systems experience thermal expansion and contraction due to variations in temperature. Flanges provide flexibility by allowing the pipes to expand and contract without putting excessive stress on the system. The flange connection accommodates thermal movements while retaining a tight and secure seal.
- Easy Integration with Other Components: Flanges can be easily integrated with valves, pumps, expansion joints, and other equipment within the piping system. This enables efficient and seamless integration of various components, ensuring smooth operation and connectivity throughout the system.
- Standardization and Interchangeability: Flanges adhere to recognized standards such as ASME, ISO, or EN, ensuring compatibility and interchangeability between different components and systems. This standardization simplifies the sourcing and procurement process, allowing for easy replacement or upgrade of flanges as needed.
Overall, the use of flanges enhances the reliability, safety, and functionality of piping systems. They provide secure and leak-tight connections, adaptability, and ease of maintenance, contributing to the efficient and trouble-free operation of industrial applications.
4. What industries are flanges mainly used in?
Flanges are used in a wide range of industries that require piping systems. Some of the main industries where flanges are commonly used include:
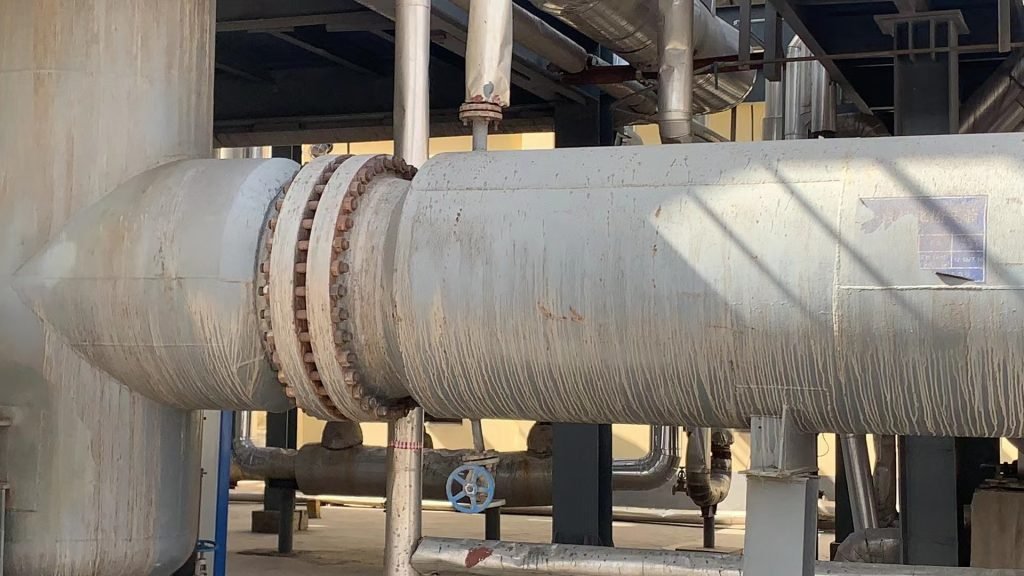

- Oil and Gas: Flanges are extensively used in the oil and gas industry for connecting pipelines, offshore platforms, refineries, and petrochemical plants. These flanges ensure safe and leak-free transportation of fluids, gases, and hydrocarbons.
- Petrochemicals: Flanges play a crucial role in petrochemical plants for connecting process equipment, reactors, heat exchangers, and storage tanks. They are used in various stages of petrochemical production, including refining, cracking, and distillation processes.
- Power Generation: Flanges are widely used in fossil fuel power plants, nuclear power plants, and renewable energy facilities. They are used to connect pipes in steam and water systems, as well as in the construction of turbines, boilers, and condensers.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: Flanges find application in water treatment plants, desalination plants, sewage treatment facilities, and municipal water distribution systems. They provide reliable connections for pipes carrying treated water, wastewater, chemicals, and sludge.
- Chemical Processing: Flanges are used in chemical plants, where they connect pipelines carrying various chemicals, acids, solvents, or corrosive substances. These flanges are designed to withstand chemical corrosion and provide leak-tight connections.
- HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning): Flanges are widely used in commercial and industrial HVAC systems. They connect pipes and ducts for the distribution of heating, cooling, and ventilation air, ensuring efficient and effective climate control.
- Pharmaceutical and Biotech: Flanges are utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing plants and biotech facilities for connecting pipelines carrying sterile fluids, gases, and pharmaceutical intermediates. These flanges adhere to strict quality and sanitary standards.
- Mining and Minerals: Flanges are employed in the mining and minerals industry for the transportation of ores, minerals, slurries, and water. They provide durable connections in pipelines used for mineral extraction, processing, and tailings management.
- Food and Beverage: Flanges find application in food and beverage production, connecting pipes carrying ingredients, beverages, and food products. These flanges are designed to meet food-grade standards, ensuring hygiene and cleanliness.
- Marine and Shipbuilding: Flanges are used in marine and shipbuilding industries for connecting pipes and systems on ships, offshore platforms, and coastal structures. They provide reliable and durable connections for various fluid and gas transport systems.
These industries represent some of the main areas where flanges are utilized, but their application extends to many other sectors that require secure and leak-tight connections in piping systems.
5. What are the types of flanges?

There are several types of flanges commonly used in piping systems. These include:
- Weld Neck Flanges: These flanges feature a long tapered hub that serves as an extension of the pipe. They are welded to the pipe, providing a strong and rigid connection. Weld neck flanges are ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
- Slip-On Flanges: These flanges have a slightly larger diameter than the pipe they are connecting to. They slip over the pipe and are then welded or fillet brazed in place. Slip-on flanges are easy to install and suitable for low-pressure applications.
- Socket Weld Flanges: These flanges are counter-bored to accept the pipe before being fillet welded around the outside. They are used for small-diameter, high-pressure applications.
- Threaded Flanges: These flanges have internal threads that match the external threads on the pipe. They are assembled by screwing them onto the pipe, providing a secure connection. Threaded flanges are suitable for low-pressure applications.
- Lap Joint Flanges: These flanges consist of two components: the stub end and the backing flange. The stub end is welded to the pipe, while the backing flange is not welded, allowing it to rotate freely. Lap joint flanges are used in applications where easy alignment and disassembly are important.
- Blind Flanges: These flanges are solid discs used to block off or seal the end of a piping system. They do not have a bore or a hub and are typically bolted to a flange of another type.
- Orifice Flanges: These flanges are used in orifice metering applications to measure the flow rate of a fluid. They have special bores or recesses to accommodate an orifice plate.
- Spectacle Blind Flanges: These flanges consist of a pair of metal discs with a solid section and a spacer section. They are used to blank off a pipe or create a temporary shut-off in a piping system.
Each type of flange has its own advantages and is suitable for specific applications. It is important to select the appropriate flange type based on the requirements of your piping system.
6. What are the different application ranges of different types of flanges?

Different types of flanges have different application ranges. Here are some common types of flanges and their typical application ranges:
- Weld Neck Flange: These flanges are widely used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications, especially in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemical, and power generation.
- Slip-On Flange: Slip-on flanges are suitable for low-pressure and low-temperature applications, such as plumbing systems, water supply, and irrigation.
- Blind Flange: Blind flanges are used to seal the end of a pipe or equipment. They are commonly used in piping systems for shutdown or isolation purposes.
- Socket Weld Flange: This type of flange is commonly used in small-diameter, high-pressure applications, such as chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
- Threaded Flange: Threaded flanges are used in low-pressure and low-temperature applications, such as plumbing systems and small-scale industries.
- Lap Joint Flange: Lap joint flanges are often used in industries that require frequent dismantling and easy access for inspection and cleaning, such as food processing and pharmaceutical industries.
- Orifice Flange: Orifice flanges are used in flow measurement applications, where an orifice plate is installed between two flanges to measure fluid flow.
- Spectacle Blind Flange: Spectacle blind flanges are used in applications where it is necessary to shut off flow temporarily, such as maintenance or repair of a pipeline section.
It’s important to note that the application range of flanges can vary depending on the specific design, materials used, and industry standards. It is recommended to consult with industry professionals or flange manufacturers for specific application requirements.
7. What are the common materials for flanges?

Flanges can be made from a variety of materials, depending on the application and the specific requirements of the piping system. Some common materials used for flanges include:
- Carbon Steel: Carbon steel flanges are widely used due to their strength, durability, and affordability. They can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for a range of applications.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel flanges are corrosion-resistant and are often used in environments where there is a risk of chemical or water corrosion. They are commonly used in food processing, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries.
- Alloy Steel: Alloy steel flanges are made from a mixture of different metals, such as chromium, molybdenum, and nickel. They offer superior strength, enhanced corrosion resistance, and excellent performance in high-temperature and high-pressure applications.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron flanges are known for their high strength and durability. They are commonly used in low-pressure and low-temperature applications, such as plumbing and heating systems.
- Brass: Brass flanges are valued for their excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. They are often used in applications where aesthetics are important, such as architectural or decorative piping systems.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC flanges are used in applications involving corrosive chemicals or where resistance to corrosion is required. They are lightweight, cost-effective, and commonly used in water and wastewater treatment plants.
- Ductile Iron: Ductile iron flanges offer strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. They are commonly used in water and sewage systems, as well as in the oil and gas industry.
The choice of flange material depends on factors like the operating conditions, pressure and temperature requirements, chemical compatibility, and cost considerations in each specific application.
8. What are the different uses of flanges of different materials?

Different materials used in flanges have specific properties that make them suitable for various applications. Here are some common materials used in flanges and their different uses:
- Carbon Steel Flanges: Carbon steel flanges are widely used in industries such as oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing. They offer good strength and are suitable for applications with high pressures and temperatures.
- Stainless Steel Flanges: Stainless steel flanges are corrosion-resistant and have high strength, making them suitable for applications where corrosion is a concern, such as in the food and beverage industry, pharmaceutical industry, and marine applications.
- Alloy Steel Flanges: Alloy steel flanges are used in applications that require high strength, excellent toughness, and resistance to corrosion and high temperatures. They are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemical, and power generation.
- Duplex Stainless Steel Flanges: Duplex stainless steel flanges offer a combination of high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. They are used in applications where resistance to stress corrosion cracking and pitting is critical, such as offshore oil platforms, chemical plants, and seawater environments.
- Brass Flanges: Brass flanges are often used in plumbing, HVAC systems, and low-pressure applications. They provide good corrosion resistance, are easy to manufacture, and offer good thermal conductivity.
- Cast Iron Flanges: Cast iron flanges are used in low-pressure and low-temperature applications. They are commonly used in plumbing systems, wastewater treatment plants, and construction projects.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Flanges: PVC flanges are lightweight, easy to install, and resistant to corrosion and chemicals. They are commonly used in irrigation systems, water supply networks, and chemical process industries.
- Titanium Flanges: Titanium flanges are used in applications where lightweight, high strength and excellent corrosion resistance are required. They find applications in the aerospace industry, chemical processing, and medical implants.
It is important to select the appropriate material for flanges based on the specific requirements of the application, including factors like temperature, pressure, fluid compatibility, and environmental conditions. Consulting with industry professionals or flange manufacturers is recommended to ensure the right material selection for specific usage.
9. what is Flange Face?
A flange face refers to the surface of a flange where it makes contact with another flange or gasket. It is the mating surface that creates a seal when two flanges are bolted together. The flange face can be flat, raised, or have a specific profile depending on the type of flange and sealing requirements.
The quality and condition of the flange face is crucial for ensuring a proper and leak-free connection. Any imperfections, such as scratches, dents, or unevenness, can negatively affect the integrity of the seal. Therefore, flange faces are carefully machined or lapped to provide a smooth and flat surface for optimal sealing performance.
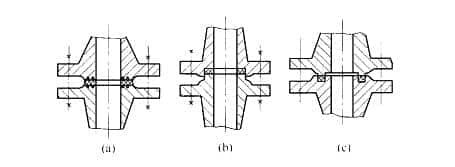
Different types of flange faces include:
- Flat Face (FF): These flange faces have smooth, flat surfaces and are typically used for low-pressure applications with non-metallic gaskets. They require additional sealing measures such as O-rings or gaskets to create a tight seal.
- Raised Face (RF): Raised face flanges have a small raised ring around the bolt holes on the flange face. This raised portion provides an additional sealing surface and enhances the ability to contain high-pressure fluids.
- Ring Type Joint (RTJ): RTJ flanges have specially designed grooves on the flange face that accommodate metal ring gaskets. These flanges are commonly used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications, such as in the oil and gas industry.
There are other specialized flange face profiles as well, depending on the specific application requirements. It’s crucial to ensure that the flange face matches the corresponding flange face on the mating flange or gasket to maintain a proper seal and prevent leakage.
10. How to choose a flange face?
Choosing the right flange face depends on several factors, including the application, pressure, temperature, type of fluid or gas being conveyed, and sealing requirements. Here are some considerations to help you choose the appropriate flange face:
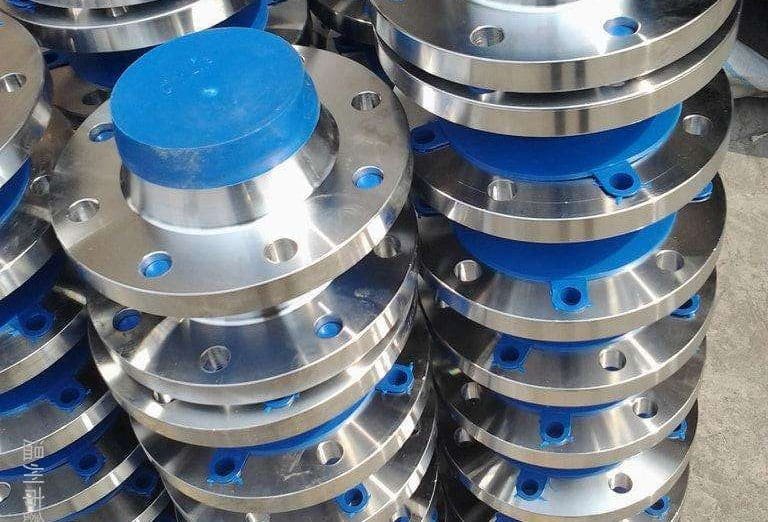

- Application and Pressure: Determine the specific application requirements and the expected pressure conditions. Different flange faces are designed to handle different pressure ranges. For example, flat face flanges (FF) are suitable for low-pressure applications, while raised face flanges (RF) or ring-type joint flanges (RTJ) are typically used for higher-pressure applications.
- Temperature: Consider the temperature of the system. High-temperature applications may require flange faces that can withstand thermal expansion or contraction. RTJ flanges, with the use of metal ring gaskets, are often preferred for high-temperature and high-pressure applications.
- Fluid or Gas Compatibility: Consider the type of fluid or gas being conveyed. Some fluids or gases may require specific flange faces or gaskets to ensure compatibility and prevent leakage. For example, corrosive fluids may require special materials or coating on the flange face to resist chemical attack.
- Sealing Requirements: Determine the desired level of seal integrity. If a higher level of sealing is required, such as in critical or hazardous applications, RTJ flanges with metal ring gaskets are often preferred due to their superior sealing capabilities. However, if a simple and cost-effective seal is sufficient, flat face flanges with appropriate gaskets or O-rings can be used.
- Industry Standards: Consider any relevant industry standards or regulations that may dictate the type of flange face to be used. Various industries, such as oil and gas, petrochemical, and water treatment, often have specific guidelines or standards for flange face selection.
Consulting with industry professionals, engineers, or flange manufacturers is advisable to ensure the correct flange face selection for your specific application. They can provide guidance and expertise based on their experience and knowledge of industry standards and best practices.
11. What kind of sealing method does the flange adopt?
Flanges typically employ various sealing methods to ensure a secure and leak-free connection. The choice of sealing method depends on the application, pressure, temperature, and fluid/gas being conveyed. Here are some common sealing methods used with flanges:

- Gaskets: Gaskets are soft, compressible materials placed between flange faces to create a seal. They fill any irregularities on the flange faces and provide a barrier against leaks. Different types of gaskets are available, such as rubber, cork, neoprene, PTFE (Teflon), spiral wound, and metal ring gaskets. The selection of the gasket material depends on factors like temperature, pressure, and the type of fluid being conveyed.
- O-Rings: O-rings are circular rubber or elastomeric seals placed in a groove on the flange face. When the flanges are bolted together, the O-ring is compressed, forming a seal between the two flange faces. O-rings provide a reliable seal for both static and dynamic applications and are commonly used in hydraulic, pneumatic, and low-pressure systems.
- Welding: Welding is used for connecting flanges in applications where a permanent and leak-free joint is required. The flanges are welded together using appropriate welding techniques and materials suitable for the specific application. Welded flanges are commonly used in high-pressure and high-temperature systems, such as in the oil and gas industry.
- Threaded Connections: In some cases, flanges may have male and female threaded connections, allowing them to be screwed together using pipe threads. The threads create a tight seal when properly tightened, eliminating the need for additional sealing methods like gaskets or O-rings. This method is commonly used in smaller pipe sizes or low-pressure applications.
- RTJ (Ring Type Joint) Gaskets: RTJ flanges use specially designed metal ring gaskets with machined grooves on the flange face. When the flanges are bolted together, the metal gasket is deformed, creating a reliable and high-pressure seal. RTJ gaskets are commonly used in critical applications, such as in petroleum refining and offshore oil drilling.
It’s essential to select the appropriate sealing method based on the specific application requirements, pressure, temperature, and the type of fluid or gas being conveyed. Consulting with industry experts or following relevant industry standards can help ensure the proper selection and installation of the sealing method for flange connections.
12. What is the size and connection diameter of the flange?
The size and connection diameter of a flange depends on the specific requirements of the application and the system it is being used in. Flanges come in a range of sizes and connection diameters to accommodate different pipe sizes and pressure ratings.

Flange sizes are typically determined by the nominal pipe size (NPS) they are intended to be used with. Common flange sizes range from ½ inch to 48 inches or even larger, although larger sizes are less common. Flanges with larger sizes are typically used in industrial applications that require higher flow rates or larger pipe diameters.
The connection diameter of a flange refers to the diameter of the pipe it is designed to connect with. It is usually specified by the nominal pipe size (NPS), which represents the approximate inside diameter of the pipe. Common connection diameters for flanges include ½ inch, 1 inch, 2 inches, 4 inches, 6 inches, 8 inches, 10 inches, 12 inches, and so on.
It’s important to note that the flange size and connection diameter should match the pipe size to ensure a proper fit and seal. Pipe standards, such as ASME B36.10 for carbon steel pipes or ASME B36.19 for stainless steel pipes, provide guidelines for pipe sizes and dimensions. Following these standards and consulting industry codes and regulations can help ensure the correct selection of flange size and connection diameter for a specific application.
13. How to choose the right size flange?
Choosing the right size flange involves considering several factors to ensure a proper fit and function within the specific application. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you choose the right size flange:

- Determine the Pipe Size: Identify the size of the pipe that the flange will connect to. This is typically specified by the nominal pipe size (NPS), which represents the approximate inside diameter of the pipe. Consult pipe standards, such as ASME B36.10 for carbon steel pipes or ASME B36.19 for stainless steel pipes, to determine the correct pipe size.
- Determine the Flange Size: The flange size should match the pipe size. Flange sizes are typically determined by the nominal pipe size they are designed for. You can refer to industry standards, such as ASME B16.5 or ASME B16.47, to find the corresponding flange size for a given pipe size. Flange sizes are usually expressed in inches, such as ½ inch, 1 inch, 2 inches, etc.
- Consider Flange Pressure Rating: Determine the maximum pressure that the flange will need to withstand in the application. Flanges have different pressure ratings, which indicate their ability to handle specific pressure levels. Ensure that the chosen flange has a pressure rating suitable for the system’s operating conditions. Pressure ratings are typically specified in pounds per square inch (psi) or classes (e.g., 150#, 300#, 600#).
- Consider Flange Material: Depending on the application, select the appropriate flange material based on factors like fluid/gas compatibility, temperature, and corrosion resistance. Common flange materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, brass, and various alloys. Refer to materials standards, such as ASTM or ASME, to choose the right material for the specific application.
- Consider Flange Type: Flanges come in various types, such as slip-on, weld neck, socket weld, threaded, or blind flanges. Consider the specific requirements of your application, such as ease of installation, maintenance, or the need for a fully sealed or blind connection, to select the appropriate flange type.
- Consult Industry Standards and Codes: It’s essential to ensure compliance with industry standards, codes, and regulations. Adhering to standards like ASME, API, ASTM, or DIN helps ensure the proper selection and installation of flanges. Consult relevant standards and guidelines specific to your industry or application to choose the right flange size.
- Seek Expert Advice: If you are unsure about the appropriate flange size for your application, it is advisable to consult with industry experts, engineers, or flange manufacturers. They can help analyze the specific requirements of your system and guide you in selecting the correct flange size.
By considering factors such as pipe size, pressure rating, material, flange type, and industry standards, you can make an informed decision and choose the right size flange for your application.
14. What is the pressure rating and temperature range of the flange?
The pressure rating and temperature range of a flange depend on various factors, including the material, design, and standard it adheres to. Here is some general information on pressure ratings and temperature ranges for common flange materials:

Carbon Steel Flanges:
- Pressure Rating: Carbon steel flanges typically have pressure ratings ranging from 150# (150 psi) to 2500# (2500 psi). Higher pressure ratings may be available for specialized applications.
- Temperature Range: Carbon steel flanges can generally handle temperatures ranging from -29°C (-20°F) to 538°C (1000°F), although the specific temperature limits may vary depending on the material grade and the presence of any additional coatings or treatments.
Stainless Steel Flanges:
- Pressure Rating: Stainless steel flanges commonly have pressure ratings ranging from 150# (150 psi) to 2500# (2500 psi). Similar to carbon steel flanges, higher pressure ratings may be available for specific applications.
- Temperature Range: Stainless steel flanges can handle a broader temperature range compared to carbon steel. The temperature range generally extends from -250°C (-418°F) to 815°C (1500°F), depending on the stainless steel grade and its corrosion resistance.
Alloy Steel Flanges:
- Pressure Rating: Alloy steel flanges can have various pressure ratings depending on the specific alloy and its composition. Common pressure ratings include 150#, 300#, 600#, 900#, 1500#, and 2500#.
- Temperature Range: The temperature range for alloy steel flanges is dependent on the alloy composition and can vary widely. Consult the specific material’s data sheet or supplier for the applicable temperature range.
It’s important to note that pressure ratings and temperature ranges can differ based on the flange size, design, and the relevant standards (such as ASME, ISO, or EN) that the flange conforms to. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications, industry standards, and relevant codes for accurate and specific pressure and temperature limits for a particular flange.
15. How to choose flanges in high-temperature and high-pressure environments?
When choosing flanges for high-temperature and high-pressure environments, several factors need to be considered to ensure reliable and safe performance. Here are some important considerations:

- Material Selection: Select flange materials designed to withstand high temperature and pressure conditions. Common materials for high-temperature applications include stainless steel (such as ASTM A182 F316/F316L or F321), alloy steel (ASTM A182 F5, F9, or F11), or superalloys (like Inconel or Hastelloy) that offer excellent high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance.
- Flange Type: Consider using raised face (RF) or ring-type joint (RTJ) flanges for high-temperature and high-pressure applications. RF flanges provide a large contact area between the flange faces and gasket, while RTJ flanges use metal ring gaskets specially designed for high-pressure sealing.
- Gasket Selection: Choose gaskets with appropriate materials and properties for high temperature and pressure. Metallic gaskets like a spiral wound or ring joint gaskets are often used in high-temperature and high-pressure situations due to their ability to withstand higher loads and elevated temperatures compared to non-metallic gaskets.
- Bolt and Nut Selection: Use high-strength, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant bolts and nuts, such as ASTM A193 Grade B7 or B16 bolts, along with corresponding heavy-duty or high-temperature lubricants. These components must be able to withstand the applied loads and operating conditions without failure.
- Flange Design: Consider flange designs that are specifically engineered for high temperatures and pressure, such as those conforming to ASME B16.5, B16.34, or B16.47 standards. These standards provide guidelines for ensuring the flanges’ structural integrity and leak-proof performance under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions.
- Thermal Expansion Considerations: Factor in the potential thermal expansion and contraction of the piping system due to high temperatures. Adequate provisions, such as expansion joints or flexible connectors, must be made to accommodate thermal movements without compromising the integrity of the flanges.
- Consultation with Experts: Seek advice from qualified engineers, flange manufacturers, or industry specialists who have experience with high-temperature and high-pressure applications. They can provide specific recommendations based on your operating conditions, including factors like temperature, pressure, fluid type, and system design.
It is crucial to follow applicable codes, standards, and guidelines, such as ASME, API, or ASTM while selecting and installing flanges for high-temperature and high-pressure environments. Additionally, considering the specific requirements of your application and seeking professional guidance will help ensure the optimal performance and reliability of the chosen flanges.
16. How to choose flanges for flammable and explosive environments?
Choosing flanges for flammable and explosive environments requires extra caution to prevent potential hazards. Here are some important considerations to keep in mind:

- Material Selection: Opt for flange materials that are suitable for flammable and explosive environments. Consider using materials like stainless steel (e.g., ASTM A182 F316/F316L) or nickel alloy (e.g., Inconel 625) as they exhibit good resistance to corrosion and high temperatures.
- Flange Rating: Ensure the flanges are designed and rated for the specific pressure and temperature conditions present in the system. Consider using flanges that comply with industry standards such as ASME B16.5 or API 6A and have appropriate pressure ratings to handle the operating conditions safely.
- Explosion-Proof Flanges: In some cases, explosion-proof flanges designed for hazardous environments may be required. These flanges feature additional safety measures such as flame arrestors or explosion-proof seals to prevent the ignition of flammable substances.
- Gasket Selection: Choose gaskets that meet the requirements for flammable and explosive environments. Non-metallic gaskets made of materials like graphite or PTFE (Teflon) can provide reliable sealing and compatibility with a wide range of fluids and temperatures.
- Tightness and Integrity: Pay attention to the tightness and integrity of the flange joint. Ensure that the gasket and flange faces are clean, smooth, and free from any debris or damage that could compromise the seal. Proper bolt tightening and torquing, following industry guidelines, are crucial for achieving a secure and leak-proof connection.
- Electrical Bonding: In certain flammable environments, electrical bonding is essential to prevent static charges that could ignite flammable substances. Ensure that the flanges have appropriate provisions for electrical bonding, such as metal-to-metal contact between flanges or conductive gaskets.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhere to applicable safety regulations, guidelines, and industry standards specific to flammable and explosive environments. Consider consulting with experts, such as fire protection engineers or safety professionals, who can provide specific recommendations for your application.
- Proper Handling and Installation: Take necessary precautions during flange handling, transportation, and installation to prevent damage to components or the release of flammable substances. Follow proper safety protocols, including the use of suitable personal protective equipment (PPE) and adherence to safe work practices.
It is crucial to consult with experts, such as process safety engineers or professionals with experience in hazardous environments, to ensure compliance with safety regulations and to select the most appropriate flanges and sealing materials for your specific flammable and explosive application.
17. What is the corrosion resistance of the flange?
The corrosion resistance of a flange can vary depending on the material it is made from. Here are some commonly used flange materials and their corrosion resistance properties:

- Carbon Steel: Carbon steel flanges are generally susceptible to corrosion. They can rust when exposed to moisture or corrosive substances, especially in harsh environments. However, carbon steel flanges can be protected through surface treatments like painting or coating.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel flanges offer excellent corrosion resistance due to the high amounts of chromium present in the material. The chromium forms a passive oxide layer on the surface of the flange, which acts as a protective barrier against corrosion. Different grades of stainless steel provide varying levels of corrosion resistance, with higher alloy content offering enhanced protection.
- Alloy Steel: Alloy steel flanges often contain various alloying elements like chromium, nickel, or molybdenum, which improve their resistance to corrosion. The corrosion resistance of alloy steel flanges depends on the specific alloy composition and can vary accordingly.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron flanges are not known for their corrosion resistance. They are prone to rusting and may require regular maintenance and surface treatments to prevent corrosion.
- Non-Metallic Materials: Flanges made from non-metallic materials like PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) or CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) offer good resistance to corrosion in certain applications. These materials are often used in non-aggressive environments or where chemical resistance is required.
It is important to consider the operating conditions, environment, and specific requirements of your application when selecting a flange material with the appropriate corrosion resistance. Consulting with an experienced flange supplier or referring to industry standards and guidelines can help determine the most suitable material for your specific needs.
18. What international standards and certifications are there for flanges?

There are several international standards and certifications that apply to flanges. Here are some of the most commonly recognized ones:
- ASME B16.5 and ASME B16.47: These are the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standards that provide dimensions, ratings, and materials for pipe flanges and flanged fittings. ASME B16.5 covers flanges up to 24 inches, while ASME B16.47 covers larger flanges in sizes 26 inches and above.
- ISO 7005-1: This International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standard specifies flange dimensions and pressure ratings for pipes and fittings in metric sizes. It includes several series such as PN6, PN10, PN16, PN25, PN40, and PN63.
- EN 1092: These European Norm (EN) standards provide requirements for flanges, including dimensions, materials, types, and pressure-temperature ratings. EN 1092-1 covers flange up to DN4000, while other EN 1092 parts cover specific aspects like gasket types, facing types, and joint faces.
- API 6A: This American Petroleum Institute (API) specification applies to flanges, valves, and fittings used in the petroleum and natural gas industries. API 6A covers wellhead and Christmas tree equipment and includes pressure ratings, material requirements, and testing procedures.
- ASTM A105/A105M: This ASTM International standard specifies the requirements for carbon steel forgings used for flanges, fittings, valves, and other piping components in high-temperature service.
- DIN EN 1759: The Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN) standard defines the dimensions, types, and materials of pipe flanges used in pipeline systems and connects flanges with externally threaded connections according to DIN ISO 228-1.
In addition to these standards, there are certifications and quality management systems that flange manufacturers may adhere to, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems, API Q1 for general requirements of petroleum industry quality systems, and various product certifications like PED (Pressure Equipment Directive) or ATEX (Atmosphères Explosibles). These certifications demonstrate compliance and adherence to specific standards and quality assurance processes.
It’s important to note that the specific standards and certifications governing flanges may vary depending on the industry, application, and geographical region.
19. How to ensure that the flange has good leak-proof performance?
To ensure that a flange has good leak-proof performance, several steps can be taken during the installation and maintenance process. Here are some key considerations:

- Proper Flange Selection: Select the appropriate flange type and material for the specific application. Consider factors such as pressure, temperature, fluid type, and compatibility to ensure the flange can handle the operating conditions effectively.
- Flange Surface Preparation: The flange mating surfaces should be clean, smooth, and free from any debris, rust, or contaminants. Use a suitable cleaning method, such as wire brushing or solvent cleaning, to ensure proper surface preparation before installation.
- Gasket Selection: Choose the correct gasket material based on the flange material, fluid characteristics, and operating conditions. Different gasket types, such as spiral wounds, ring joints, or soft-cut gaskets, have specific properties that can enhance leak-proof performance.
- Proper Gasket Installation: Install the gasket correctly, ensuring it is centered and properly seated between the flange faces. Follow manufacturer guidelines or industry standards (such as ASME B16.20 for metallic gaskets) for correct gasket placement and compression.
- Bolt Tightening: Proper bolt tightening is crucial for maintaining a leak-free connection. Use a calibrated torque wrench or tensioning equipment and follow the recommended bolt-tightening sequence and torque values specified for the flange size and class.
- Flange Alignment: Ensure proper alignment of mating flanges to avoid any misalignment or twisting that could compromise the leak-proof performance. Misalignment can place excessive stress on the gasket and result in leaks.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly inspect the flanges for signs of leakage, deterioration, or damage. If any leaks are detected, address them promptly by tightening bolts, replacing gaskets, or taking appropriate corrective measures.
- Compliance with Standards: Follow industry standards and specifications, such as ASME B16.5 or API 6A, for proper flange installation, gasket selection, and maintenance procedures to ensure leak-proof performance.
It is essential to consult with qualified professionals, such as piping engineers or experienced flange suppliers, for guidance on specific installation procedures, gasket selection, and maintenance practices based on your application requirements.
20. Will the use of flanges increase the cost of the project?
The use of flanges in a project can impact the overall cost, but it is important to consider the specific requirements and circumstances of the project. Here are some factors to consider regarding the cost of using flanges:

- Material and Quality: The material and quality of flanges can vary, impacting the cost. Flanges made from specialized materials or with higher quality standards may be more expensive than standard options.
- Size and Pressure Ratings: Flanges come in various sizes and pressure ratings, and the cost may increase with larger or higher-pressure flanges. High-pressure applications may require more robust and expensive flanges.
- Quantity and Complexity: The number and complexity of flange connections in a project can influence the cost. Numerous connections or intricate piping systems may require a higher quantity of flanges and result in increased costs.
- Customization and Special Requirements: If the project demands custom-designed or specialized flanges, such as those with unique dimensions or specific certifications (e.g., food-grade or high-temperature resistance), the cost may be higher due to the additional manufacturing or testing processes involved.
- Installation and Labor Costs: The installation of flanges requires skilled labor and may involve additional costs for alignment, bolting, welding, or sealing. Complex installations or tight project timelines can increase labor costs.
- Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs: While not directly related to the initial project cost, it is essential to consider the long-term maintenance and lifecycle costs associated with using flanges. Quality flanges may require less frequent maintenance or replacement, reducing overall costs in the long run.
It is crucial to assess the specific project requirements, including the factors mentioned above, and compare various options to determine the most cost-effective solution. Collaboration with engineers, designers, and suppliers can help in selecting the appropriate flanges that meet both technical needs and cost considerations.
21. Why is the flange price of Chinese flange manufacturers so cheap?
The lower prices of Chinese flange manufacturers can be attributed to several factors:

- Lower Labor Costs: China has a large labor force, and labor costs are comparatively lower than in many other countries, especially in developed economies. This lower labor cost can contribute to lower production costs and, consequently, lower prices for products like flanges.
- Economies of Scale: Chinese flange manufacturers often operate at a larger scale due to the size of the domestic market and the demand for flanges both domestically and internationally. This allows them to benefit from economies of scale, reducing production costs and enabling them to offer competitive prices.
- Raw Material Availability: China has abundant reserves of resources like steel, which is a key material used in flange manufacturing. The availability of these raw materials within the country can help reduce procurement and transportation costs, contributing to lower overall production costs.
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Chinese manufacturers, especially those with years of experience and established production facilities, have developed efficient manufacturing processes and improved technologies. This enables them to produce flanges more efficiently and cost-effectively, leading to lower prices.
- Government Policies: The Chinese government has implemented various policies to support manufacturing industries, including the flange manufacturing sector. These policies may include incentives, tax benefits, and subsidies, which can further reduce production costs and contribute to lower prices.
It is important to note that while Chinese flange manufacturers may offer lower prices, it’s still essential to ensure the quality of their products. Conducting proper due diligence, as mentioned earlier, is crucial to selecting a reputable supplier who can provide high-quality flanges at competitive prices.
22. Is the quality of flanges purchased from China guaranteed?
The quality of flanges purchased from China, or any other country for that matter, is not inherently guaranteed. It is essential to maintain due diligence and conduct thorough research and quality assurance processes when purchasing flanges from any supplier, including those in China. Here are some key considerations:

- Supplier Selection: It is crucial to carefully evaluate and choose reputable suppliers with a proven track record of manufacturing and supplying high-quality flanges. Look for suppliers with certifications, such as ISO 9001 or API Q1, which demonstrate adherence to international quality management standards.
- Quality Control and Inspection: Implement stringent quality control measures throughout the procurement process. Perform factory and product inspections to ensure that manufacturing processes meet the required standards and that the finished flanges conform to specifications, performance requirements, and industry standards.
- Material Traceability: Verify the source and quality of materials used in the manufacture of flanges. Ensuring proper material traceability can help mitigate the risk of using substandard materials and provide assurance of the flanges’ quality and performance.
- Compliance with Standards: Confirm that the flanges meet relevant industry standards, such as ASME, ASTM, ANSI, or EN, depending on the specific requirements of your project. Compliance with these standards ensures the flanges’ reliability, safety, and compatibility with the intended application.
- Warranty and After-Sales Support: Inquire about warranty policies and after-sales support provided by the supplier. A reputable supplier should offer warranties, product support, and assistance in case of any issues or defects in the supplied flanges.
- Customer Reviews and References: Seek feedback from other customers who have previously purchased flanges from the supplier, especially those who have used flanges in similar applications or industries. Customer reviews and references can provide valuable insights into the quality and performance of the supplier’s products.
While there are many reputable and reliable flange manufacturers in China, it is important to conduct thorough due diligence and quality assurance measures to minimize the risk and ensure the quality of the flanges you purchase.
23. How to purchase flanges from Chinese flange manufacturers?
To purchase flanges from Chinese flange manufacturers, follow these steps:

- Identify your Flange Requirements: Determine the specific requirements for the flanges you need, such as size, material, pressure rating, flange type, and any other specifications. This will help you communicate your requirements effectively to the Chinese manufacturers.
- Research Potential Suppliers: Conduct thorough research to identify potential Chinese flange manufacturers. Utilize online directories, trade platforms, industry associations, and referrals from colleagues or industry contacts to find reputable suppliers. Some popular platforms to find Chinese suppliers include Alibaba, Global Sources, and Made-in-China.
- Contact Suppliers: Reach out to the identified suppliers to inquire about their flange products and request a quote. Provide detailed specifications and quantities to receive accurate pricing information. Communication can be conducted through email, phone, or online messaging platforms.
- Request Sample and Product Information: Before placing a large order, ask for samples of the flanges from the shortlisted suppliers. Evaluate the samples based on your requirements and quality standards. Also, request product catalogs, technical specifications, and any other relevant documentation to assess the manufacturers’ capabilities.
- Verify Supplier Credentials and Quality Control Processes: Research the credibility and reputation of the shortlisted suppliers. Look for certifications like ISO 9001, API Q1, or other industry-specific certifications that demonstrate their adherence to quality management standards. Verify their quality control processes, material traceability, and compliance with relevant industry standards.
- Negotiate Terms and Pricing: Engage in negotiations with the suppliers to determine product pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and other relevant factors. Compare offers from different suppliers to get the best value for your requirements.
- Visit the Factory or Conduct Product Inspections: If feasible, consider visiting the manufacturing facilities of the selected suppliers to assess their capabilities and quality control measures. Alternatively, hire a third-party inspection agency to conduct factory inspections and product inspections before shipment.
- Finalize Purchase and Delivery: Once you are satisfied with a particular supplier, finalize the purchase agreement, including terms and conditions, payment arrangements, shipping details, and any other necessary contractual obligations. Ensure that the delivery schedule aligns with your project timeline.
- Quality Assurance and After-Sales Support: Maintain regular communication with the supplier during the production process to ensure quality assurance. Consider requesting quality inspection reports or certifications for the batch of flanges being delivered. Establish the after-sales support available for any issues, warranty claims, or technical assistance required.
It is crucial to conduct thorough due diligence, communicate clearly with suppliers, and follow robust quality control processes to ensure a successful purchase and to receive high-quality flanges from Chinese manufacturers.
24. When do we need to customize the flange?
Customizing flanges may be necessary in the following scenarios:

- Non-Standard Specifications: If your project requires flanges with specifications that are not readily available in standard flange offerings, customization may be required. This could include unique dimensions, materials, pressure ratings, or specialized features.
- Industry-Specific Requirements: Certain industries, such as oil and gas, chemical processing, or maritime, may have specific requirements for flanges due to safety, corrosion resistance, or structural considerations. Customized flanges may be necessary to meet these industry-specific requirements.
- Challenging Environments: If your application involves extreme temperatures, high pressures, corrosive substances, or hazardous environments, you may need customized flanges with specific material compositions and designs to ensure optimal performance and safety.
- Retrofitting Existing Systems: When modifying or retrofitting an existing system, standard flanges may not fit the particular requirements due to variations in piping systems, connections, or layouts. Customized flanges may be necessary to ensure compatibility and successful integration into the system.
- OEM and Specialty Equipment: Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) often require customized flanges designed to fit their specialized equipment or proprietary designs. Customized flanges may be necessary for OEMs to maintain the compatibility and performance standards of their equipment.
- Project-Specific Requirements: Each project may have unique needs and specifications that standard flanges may not meet. Customized flanges can be designed to fulfill these project-specific requirements, ensuring proper functionality and reliability.
When considering customization, it is important to work closely with reputable manufacturers or suppliers who have experience in designing and producing customized flanges. They should have the engineering expertise and capabilities to understand your requirements, provide technical support, and deliver high-quality custom flanges that meet your needs.
25. What are the processes of custom flanges?
The processes involved in customizing flanges can vary depending on the specific requirements and complexity of the project. However, here are some common steps involved in the custom flange manufacturing process:

- Requirement Gathering: Work closely with the manufacturer to discuss and finalize your specific flange requirements. Provide detailed specifications such as size, dimensions, material type, pressure rating, flange type, connection type, and any other necessary details.
- Design and Engineering: The manufacturer’s engineering team will create 3D models and design drawings based on your requirements. They will consider factors such as structural integrity, industry standards (e.g., ASME, DIN), compatibility with the intended system, and any specific project constraints.
- Material Selection: Based on the design requirements, the material for the custom flanges is chosen. It could be a standard material like carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel, or it might require a specialized material with specific properties such as high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, or wear resistance.
- Manufacturing Process Selection: The manufacturer will determine the most suitable manufacturing processes to produce the custom flanges. This could include forging, machining, casting, or a combination of processes depending on the material, design complexity, and quantity required.
- Production: The custom flanges are manufactured following the chosen process. This involves shaping the material, removing excess material through machining processes, heat treatment if required, and ensuring dimensional accuracy according to the design specifications.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: To ensure the flanges meet the required standards and specifications, various tests and inspections are conducted. This can include dimensional inspections, non-destructive testing (NDT), pressure testing, visual inspection, material analysis, and any other tests deemed necessary.
- Finishing and Surface Treatment: Depending on requirements, the custom flanges may undergo additional finishing processes such as machining, polishing, coating (e.g., painting, galvanizing), or surface treatments to improve corrosion resistance or enhance aesthetic appearance.
- Documentation and Certification: The manufacturer provides documentation including material test reports (MTRs), inspection reports, certificates of compliance, and any other relevant certifications required for documentation and traceability purposes.
- Packaging and Shipping: The custom flanges are properly packaged to ensure protection during transportation. Packaging methods may include wooden crates, wooden pallets, or other suitable methods depending on the size, weight, and fragility of the flanges. The shipping method is determined based on your requirements.
Custom flange manufacturing involves careful coordination between the manufacturer and the customer to ensure accurate design, quality manufacturing, and meeting the required specifications. It is important to maintain a close collaborative relationship with the manufacturer throughout the process to ensure the successful customization of flanges.
26. What kind of after-sales service and support does the flange supplier provide?
The after-sales service and support provided by a flange supplier can vary depending on the company and its specific policies. However, here are some common after-sales services and support that a flange supplier may provide:

- Technical Assistance: The supplier may offer technical support to address any queries, concerns, or technical issues related to the flanges. This can include providing guidance on installation, maintenance, troubleshooting, or any other technical aspects.
- Warranty: Flange suppliers often offer warranties on their products to ensure customer satisfaction. The warranty terms and conditions may vary, but it typically covers any defects in the product or workmanship. The supplier may repair or replace defective flanges within the warranty period.
- Product Training: Some suppliers provide product training sessions or workshops to educate customers on the proper use, handling, and maintenance of the flanges. This can help customers maximize the performance and lifespan of the flanges.
- Spare Parts Supply: A reliable flange supplier may offer spare parts for their flanges to support ongoing maintenance and repairs. They can provide genuine replacement parts as needed, ensuring the long-term functionality of the flanges.
- Customization Support: If you require custom flanges or modifications to standard products, a good supplier will have the capabilities to support your customization needs. They can assist with design, engineering, and manufacturing processes to meet your specific requirements.
- Inventory Management: Some suppliers offer inventory management services to help you maintain an adequate stock of flanges. This can include maintaining safety stock levels, providing periodic stock reports, and managing supply chain logistics to ensure timely delivery of flanges when needed.
- Prompt Communication: A reliable supplier will have responsive communication channels to address customer inquiries, requests, or issues in a timely manner. Whether through email, phone, or online platforms, efficient communication is crucial for providing excellent after-sales support.
- Continuous Improvement: Good flange suppliers strive for continuous improvement and value customer feedback. They may have systems in place to collect customer feedback, suggestions, and complaints, which they can use to enhance their products and services.
It’s important to note that the specific after-sales services and support provided can vary from supplier to supplier. Prior to making a purchase, it is recommended to inquire about the after-sales support offerings and clarify any questions or concerns you may have.
Author: Lewis Liu
Hello, my name is Lewis Liu, and I’m a professional sales engineer with over a decade of expertise in the flange fittings sector.
I am quite informed about flange selection, installation, and maintenance. I am passionate about providing customers with the greatest solutions for keeping their pipeline systems running smoothly, safely, and dependably.
If you have any queries or concerns concerning flange fittings for your pipelines, whether they are about selection, material choice, specification requirements, or anything else, please contact me at any time. I am dedicated to providing expert advice and assistance to help you make educated decisions and reach your objectives.

