Socket Weld Flanges: Features, Uses, and Material Guide
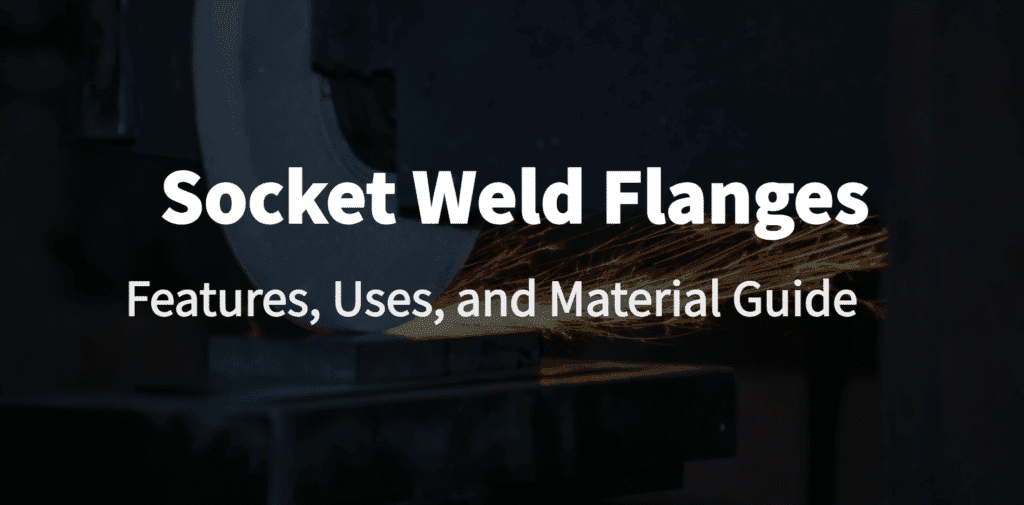
Socket weld flanges are essential elements of pipe systems requiring considerable strength and longevity to sustain high pressure and high temperature, ensuring connections that render repetitive leak-proof.
Usually used in small bore pipes where tight seals and structural integrity are critical, these flanges are commonly used. Socket weld flanges permit the insertion of the pipes into an area recessed before welding, eliminating leak risks and providing durability.
Understanding Socket Weld Flanges
Socket Weld Flanges (SW) are similar to Slip-on Flanges (SO). The difference is that there is an extra piece in the middle.
Socket weld flanges are special pipe fittings used to form robust, leak-proof joints within piping systems. Unlike other flange types, they feature a recessed socket in which the pipe is placed for welding, thus giving it more security and precision in the joint.
This recessed design makes them ideal for smaller-diameter pipelines where high structural integrity with minimum leakage is required.
Socket weld flanges are generally used in systems where flow pressure is moderate to high and where strong, vibration-resistant connections are of paramount importance.
First, the flange is fitted onto the pipe, then a fillet weld is performed around the outer edge, making a permanent and strong connection.
The method of welding provides for a smooth bore with minimal pressure drops or turbulence within the pipeline.
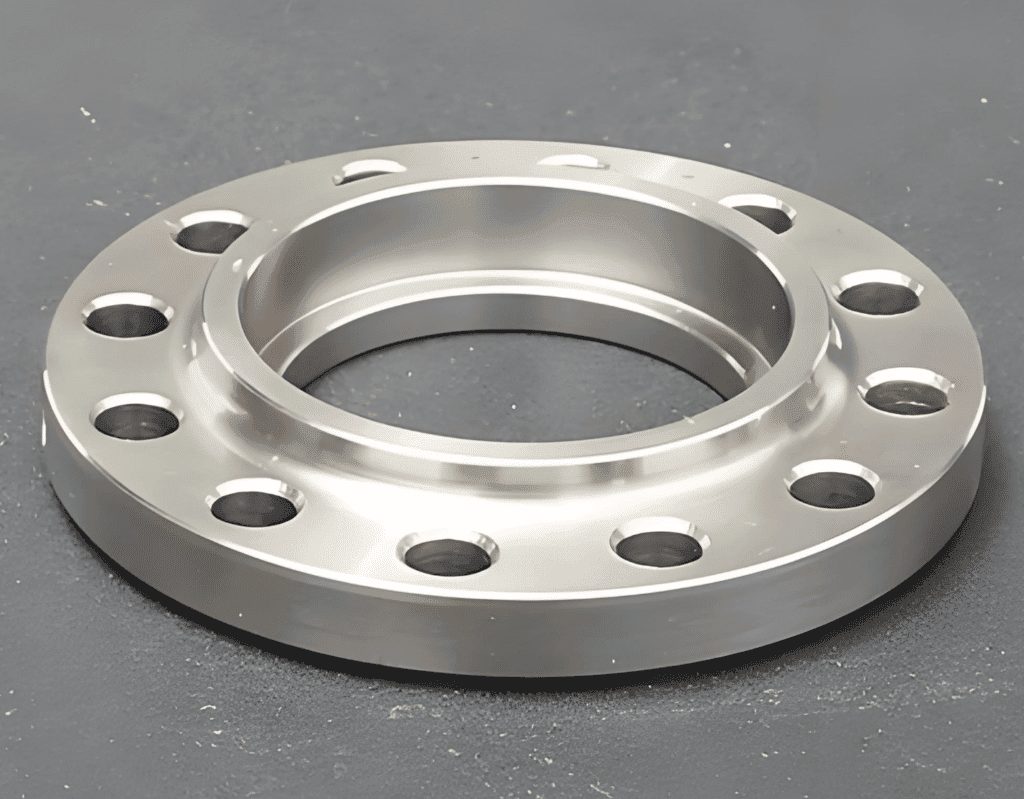
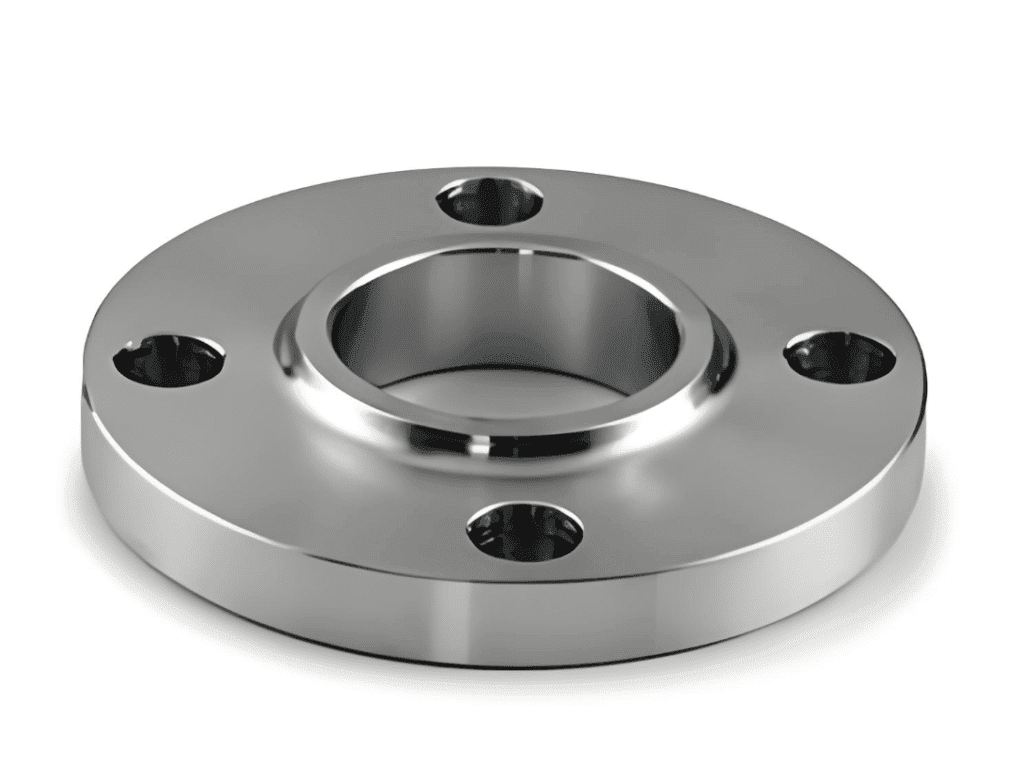
Key Features of Socket Weld Flanges
Design and Construction
Socket weld flanges have a precise machine-designed socket, or recess, for a pipe end. Usually, socket depth is 1.25 pipe wall thickness and provides optimum welding condition and joint strength.
The flange face possesses a raised or flat surface with bolt holes arranged in a standardized pattern according to pressure class requirements.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
These flanges are manufactured to various pressure class ratings, typically from Class 150 through Class 1500.
The pressure-temperature ratings are provided by both the material of the flange and the appropriate design code, such as the ASME/ASNI B16.5.
Because of their joint strength, socket weld flanges will generally accept higher pressure ratings than threaded connections.
Welding Characteristics
Socket weld flanges are designed for weldability and machined for a specific socket depth, allowing proper heat distribution during welding. The welding procedure involves welding a fillet weld around the circumference of the pipe at the socket opening.
By creating a full-strength joint, using this method means the stress is distributed across the connection, and best welding practices leave a particular gap (approximately 1/16 inch) between the pipe end and the socket bottom because it allows proper heat distribution and prevents stress concentration.
Safety Characteristics
Socket weld flanges have a number of features that enhance safety. The welded joint eliminates the chance of mechanical loosening, which can occur in threaded connections, thus offering better safety for high-vibration applications. The design also includes proper characteristics of stress distribution that help avoid joint failure under normal operating conditions.
Applications of Socket Weld Flanges
Instrumentation Lines
Socket weld flanges are widely used in instrumentation systems to connect measuring devices and control equipment to process lines. These flanges are very useful in instrumentation due to the following reasons:
- Ensure secure connection for pressure gauges, flow meters, and other such sensitive instruments
- Joints that are vibration-resistant protect fragile instrument connections
- Easy to remove during maintenance and replacement.
- Accurate process measurements and control signals requiring reliable sealing
Process Sampling Systems
Sampling points in industrial processes need reliable, leak-free connections that are easy to maintain. Socket weld flanges have excellent performance in sampling system applications due to the following reasons:
- Internal surfaces that are clean, crevice-free, and minimize sample contamination
- It is particularly easy to integrate with sample coolers and analysis equipment.
- High-strength connections can withstand frequent sample valve operation without disconnects or breaks.
- Various analytical instruments and sampling devices compatibility.
Small Bore Piping Systems
For small bore pipe applications (usually 2 cm and smaller), socket weld flanges are often the best choice. Considering:
- Better joint strength than threaded connections
- High-cycle fatigue applications have excellent performance
- Cost-effective installation in complex small bore piping networks
- Performance in auxiliary service lines and branch connections.
High-Pressure Service Lines
Socket weld flanges show excellent performance in high-pressure applications where system integrity is critical. These include, but are not limited to:
- Hydraulic power systems operating under elevated pressure
- Chemical high-pressure injection lines
- Compressed gas distribution systems
- Maximum joint reliability critical process lines
- Power generation secondary cooling systems
Steam Systems
The properties of socket weld flanges provide certain advantages in steam service applications that make them especially suitable for such operations:
- Provide excellent resistance to thermal cycling effects
- Superheated and saturated steam service performance.
- Thermal expansion accommodation built in.
- Condensate return lines with high reliability
- Steam tracing system robust connections
Material Guide for Socket Weld Flanges
Socket weld flanges are essential equipment for different factories, therefore choosing the right material is very important. Here are some common socket weld flange materials and their corresponding mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, plus typical applications.
| Material | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Temperature Range (°C) | 515-620 | Suited For |
| Carbon Steel (ASTM A105) | 250 – 485 | 485 – 760 | -29 to 425 | Low | Oil & gas pipelines, water distribution systems. |
| Stainless Steel (ASTM A182 F304) | 205 – 310 | 515 – 620 | -196 to 815 | Moderate | Food processing, general industrial applications. |
| Stainless Steel (ASTM A182 F316) | 205 – 310 | 515 – 620 | -196 to 815 | High | Marine environments, chemical processing. |
| Alloy Steel (ASTM A182 F11/F22) | 310 – 415 | 590 – 795 | -29 to 600 | Moderate | High-pressure steam systems, power generation. |
| Duplex Stainless Steel (ASTM A182 F51/F53) | 450 – 550 | 620 – 850 | -50 to 300 | Very High | Offshore oil & gas, petrochemical applications. |
| Nickel Alloys (ASTM B564 N06625/N08825) | 350 – 450 | 830 – 950 | -200 to 1000 | Exceptional | Aerospace, chemical industries, high-temperature applications. |
| Copper-Nickel (Cu-Ni) (ASTM B151) | 105 – 170 | 275 – 415 | -196 to 300 | High | Shipbuilding, desalination plants, offshore piping. |
Types of Socket Weld Flanges
Raised Face (RF) Socket Weld Flanges
Raised Face (RF) Socket Weld Flanges have a raised flange bore on the face with the gasket sitting on the raised surface. This design improves the sealing performance suitable for medium- to high-pressure applications. Therefore, most of them are the flanges that are used in chemical processing, oil and gas, power generation, etc. so that they provide good and reliable leak-proof connections.
Flat Face (FF) Socket Weld Flanges
FF Socket Weld Flanges have a flange face surface that is normally a flat gasket surface. This design is suitable for use on equipment that is metallic cast iron, and so on, or other materials that you do not want to damage when joining. They are preferred in waterworks, HVAC systems and low-pressure pipelines because of their ability to prevent flange distortion.
Ring-Type Joint (RTJ) Socket Weld Flanges
Ring-Type Joint (RTJ) Socket Weld Flanges with a precision machined groove to hold metal ring gasket to provide a metal-to-metal seal. The resistance to leakage under high-pressure and high-temperature is superior to other designs. RTJ flanges are used mostly in the petrochemicals, offshore drilling and high-temperature steam systems industries.
Reducing Socket Weld Flanges
Reducing Socket welding Flanges are intended to join pipes with different diameters. Through a smaller socket bore, these components eliminate the need for additional reducers, simplifying the pipeline layout and lowering installation costs. Because of their compactness, these flanges are widely used in systems where space optimization is critical, such as instrumentation lines, process sampling systems, and small bore piping networks.
YANHAO: Trusted Supplier of Socket Weld Flanges
As a trusted Chinese flange supplier, YANHAO is known for providing high-quality socket weld flanges that perfectly meet the high requirements of different industries.
YANHAO flanges are designed to be precise, durable, and have high performance in the face of extreme pressure, extreme temperature, and corrosive environments. To ensure each product is manufactured to the highest standards and reliable and leak-proof for critical applications.
YANHAO is your partner for durable and cost-effective socket weld flange solutions in oil and gas, chemical processing, or power generation.
To Conclude
Socket weld flanges have a critical function in guaranteeing the validity and effectiveness of piping systems in different industries.
The design and construction of these help to provide a reliable method of connecting pipes in small bore and high pressure and critical service applications. However, selecting a socket weld flange type and materials helps you get superior performance and safety.
Partnering with trusted suppliers such as YANHAO ensures that you will get the best quality products to meet your needs.
Other Types of Flanges

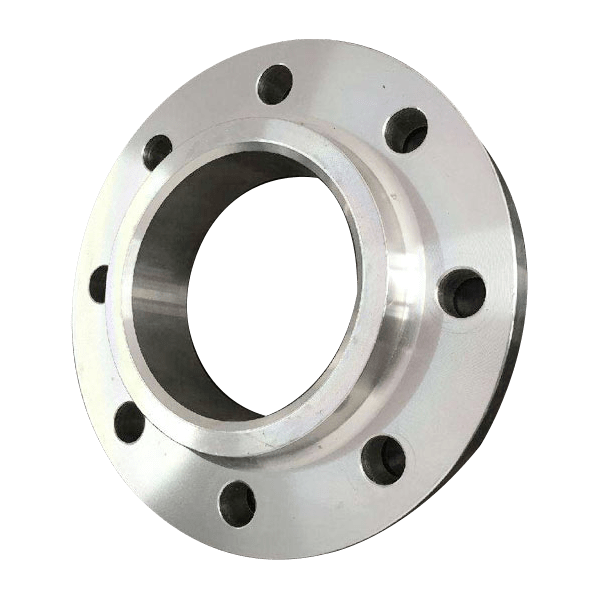
Weld Neck Flanges (WN)
WN flange, also known as a trapped hub flange or high-hub flange, is a high-stress-containing flange. Its circular fitting component, the rim, is fitted around the circumference.
China welding neck flange products >>

Slip-on Flanges (SO)
Slip-on flanges, as the name shows, can be easily slipped onto the end of a pipe or fitting and then welded in place. It usually has a flat face and a protruding face.
China slip-on flange products >>

Socket Weld Flanges (SW)
Socket Weld Flanges (SW) are similar to Slip-on Flanges (SO). The difference is that there is an extra piece in the middle.
China socket weld flange products >>

Blind Flanges (BF)
Blind flange is also called flange cover. It is a flat, circular plate used to cover the ends of pipes, valves, or joints.
China blind flange products >>
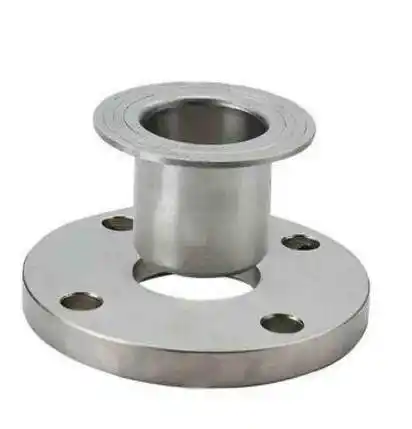

Lap joint flange (LJ)
Consisting of two components: a stub end and a lap joint ring flange. The respective stub end is slid into the flange’s bore, and the stub end is joined to the pipe through butt welding.
China lap joint flange products >>
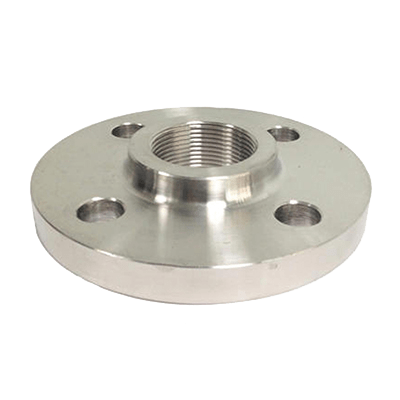

Threaded Flanges (TF)
Threaded flanges are pipe flanges with internal threading to match external threads on a pipe. The installation does not involve welding
China threaded flange products >>
Author: Lewis Liu
Hello, my name is Lewis Liu, and I’m a professional sales engineer with over a decade of expertise in the flange fittings sector.
I am quite informed about flange selection, installation, and maintenance. I am passionate about providing customers with the greatest solutions for keeping their pipeline systems running smoothly, safely, and dependably.
If you have any queries or concerns concerning flange fittings for your pipelines, whether they are about selection, material choice, specification requirements, or anything else, please contact me at any time. I am dedicated to providing expert advice and assistance to help you make educated decisions and reach your objectives.

