Flange Dimensions: What Do ID and OD Mean?
When we look at flange dimensions, we often see the unit identifiers ID and OD. What do they mean? This article will tell you.
oD and iD meaning
In flange nomenclature, OD denotes outer diameter and ID denotes inner diameter. You can understand the relationship between OD and ID from the picture below.
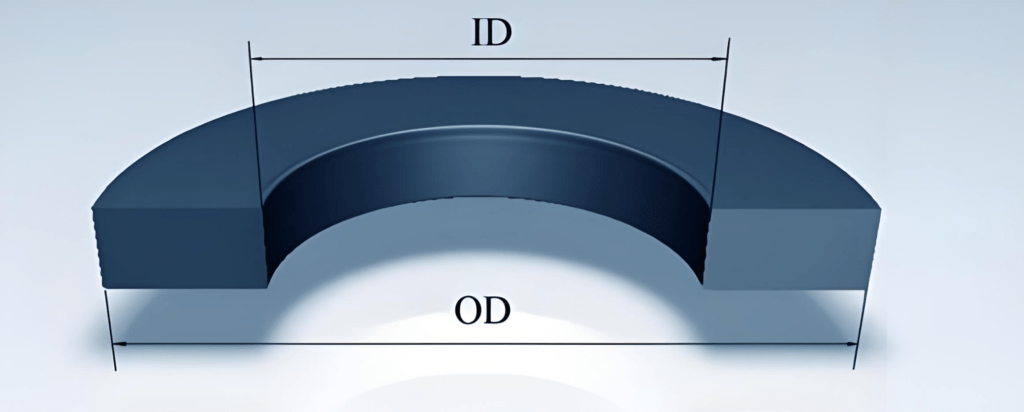
OD (Outside Diameter)
The OD (outer diameter) of a flange means the measured diameter of its outermost edge. This is a significant parameter on flange design and engineering drawings since it dictates the flange’s size and the pipe or equipment it can accommodate.
ID (Inside Diameter)
ID (Inner Diameter) means the diameter of the flange’s central hole. This dimension is crucial to ensuring that the flange can accommodate a specified pipe size because the pipe must pass through the flange’s center hole.
Note: Whether it is OD or ID, these two are dimensions with actual measurement meaning. Following them is a number and a unit, typically in millimeters (mm). For example, OD 60 mm and ID 40 mm mean that the outer diameter of the tube is 60 millimeters and the inner diameter is 40 millimeters.
These two dimensions are crucial for ensuring that the flange can be properly placed and is compatible with the pipe system or equipment. Flanges are commonly used to connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other components. They use bolts and screws to connect two flanges and gaskets to seal the connection.
The outer diameter (OD) is used to determine the size of fittings (such as flanges or connectors) fitted on the edges of the pipe. It also helps define the pipe’s strength and resistance to external forces, especially in applications involving Schedule 40 or Schedule 80 pipe.
For example, in construction, the outside diameter is critical for determining the proper pipe size to withstand the structure’s weight and pressure.
Conversely, the inner diameter (ID) is critical for defining the pipe’s flow capacity. The carrying capacity of a pipe is exactly proportional to its inner diameter. For example, in pipeline applications, knowing the ID ensures that water or other fluids flow effectively through the pipe.
The practical application of outer and inner diameters extends across multiple sectors. In the oil and gas business, determining the outside diameter is critical for selecting pipes that can endure harsh environmental conditions and high pressure. On the other side, inner diameter measurements are critical in industries such as heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), where exact flow capacity is required for proper ventilation or cooling.
You may also see these dimension labels: DN and NPS
DN (Nominal Diameter)
DN stands for nominal diameter, which is a general term for the sizes of pipes and fittings in a piping system. The nominal diameter is a convenient round number for reference and does not have a strict relationship with the actual manufacturing dimensions. Normally the numbers following the letters DN do not represent a measured value and cannot be used for calculation purposes.
NPS (Normal Pipe Size)
NPS stands for Nominal Pipe Size. It is a piping standard issued by the American National Standards Institute. The ratio of the pipe’s inside diameter or outside diameter (OD) to its pipe wall thickness serves as a measure of the external diameter in the NPS notation, where the unit of measurement is inches (inch). This standard helps in defining the diameter (OD) and schedule of the pipe, such as Schedule 40 or Schedule 80 pipe, which are commonly used in industrial applications.
For example, NPS 1/2 indicates that the nominal pipe size of the pipe is 1/2 inch. This size designation helps in selecting the appropriate pipe wall thickness and schedule for specific applications, ensuring compatibility and safety.
In short, DN and NPS (Nominal Pipe Size) are both standard size designation methods used to describe the dimensions of pipes or pipe fittings, but they are applicable to European and North American piping standards, respectively. DN uses millimeters as the unit, while NPS uses inches as the unit, and both aim to ensure good interchangeability of pipes and fittings.
The main difference between them lies in the units used: DN uses millimeters as the unit, while NPS uses inches as the unit.
Both standards aim to ensure good interchangeability of pipes and fittings produced by different manufacturers, facilitating design and engineering applications.
YANHAO’s Expertise in Pipe Diameter Identification

YANHAO has vast knowledge and competence in properly determining pipe dimensions for a variety of industries. Our professionals are well qualified and understand each industry’s unique requirements and challenges.
Whether in the oil and gas business, chemical processing, construction, or any other industry, we have the experience to precisely select pipe diameters to match each customer’s specific demands.
Yanhao employs innovative instruments and technology to improve the accuracy and efficiency of pipe diameter identification. We use cutting-edge measuring technology, such as laser scanners and digital imaging systems, to assure exact and non-destructive results.
These technologies allow us to collect extensive data, evaluate complex geometries, and offer precise measurements fast and efficiently.
Customers can rely on our services with confidence, knowing that they will receive reliable information to make educated decisions and ensure project success.
Author: Lewis Liu
Hello, my name is Lewis Liu, and I’m a professional sales engineer with over a decade of expertise in the flange fittings sector.
I am quite informed about flange selection, installation, and maintenance. I am passionate about providing customers with the greatest solutions for keeping their pipeline systems running smoothly, safely, and dependably.
If you have any queries or concerns concerning flange fittings for your pipelines, whether they are about selection, material choice, specification requirements, or anything else, please contact me at any time. I am dedicated to providing expert advice and assistance to help you make educated decisions and reach your objectives.

