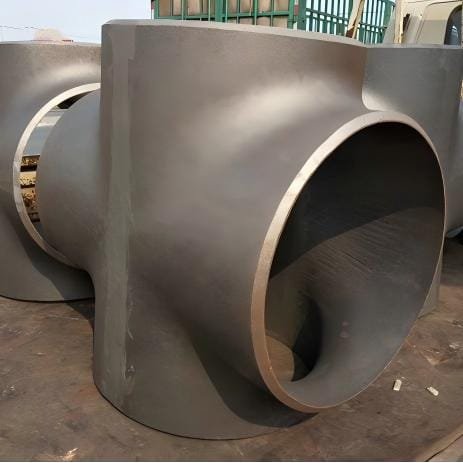
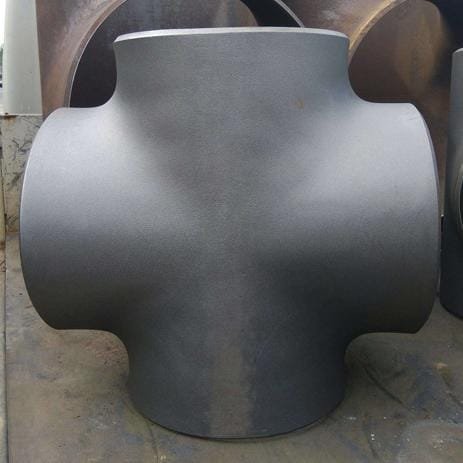
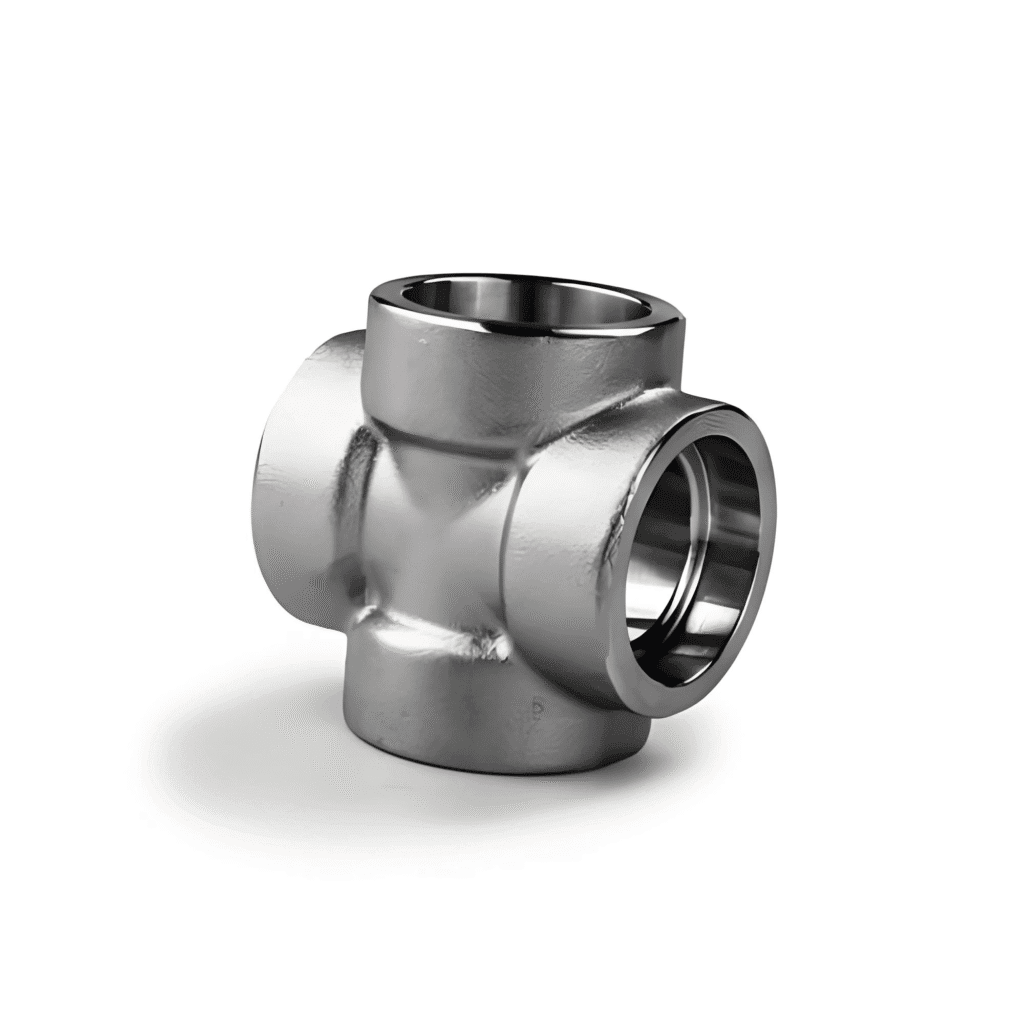
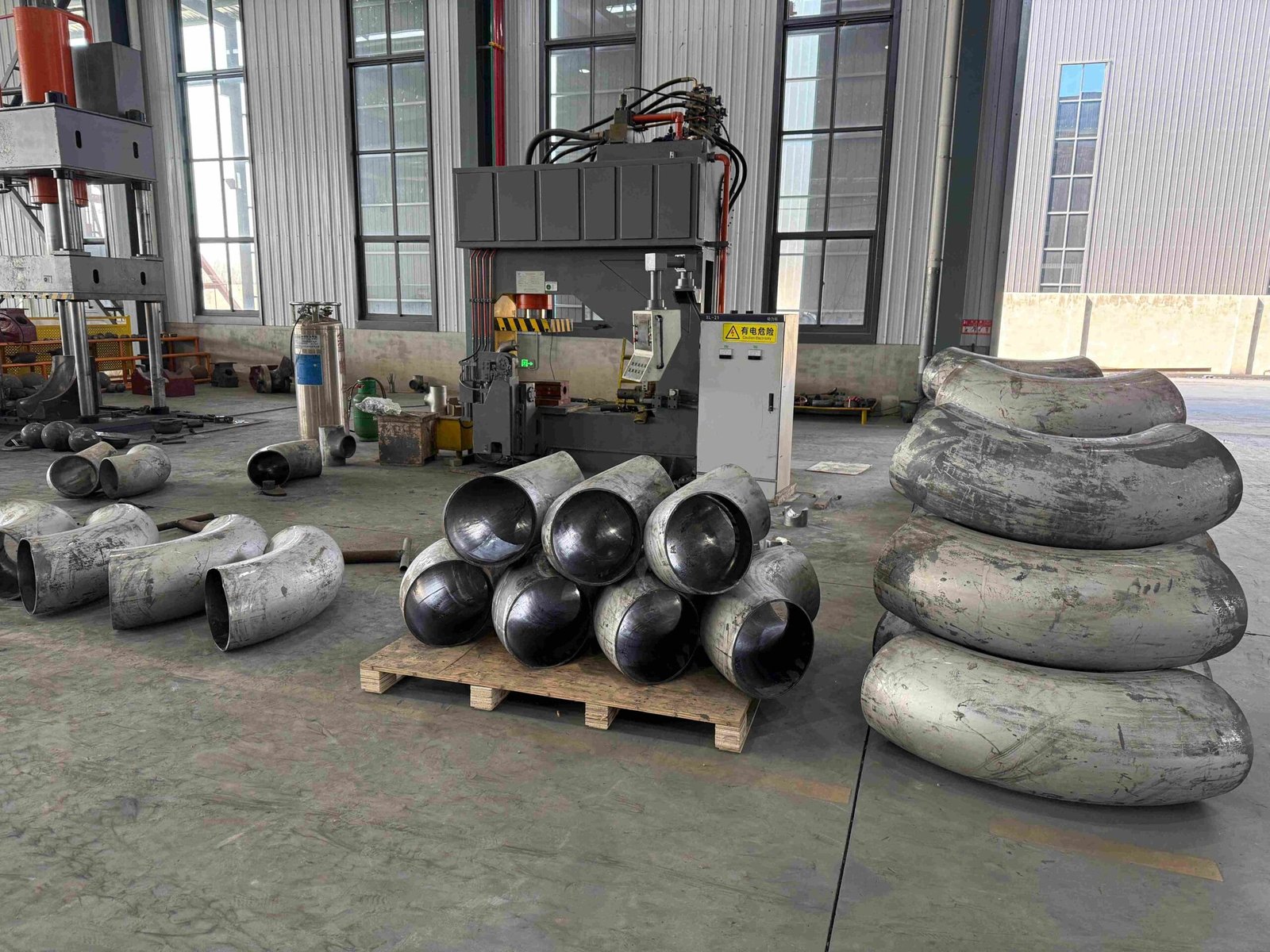
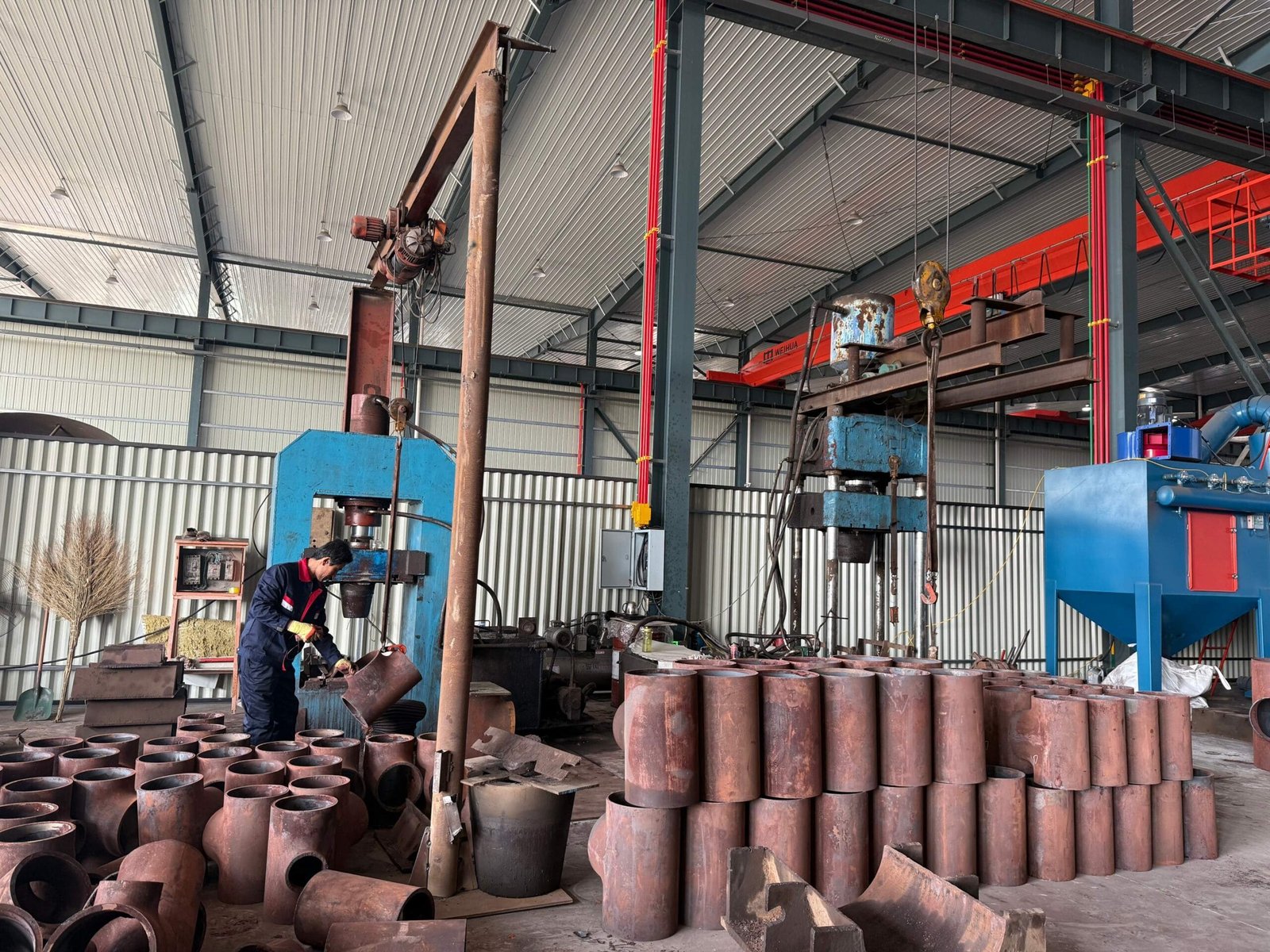
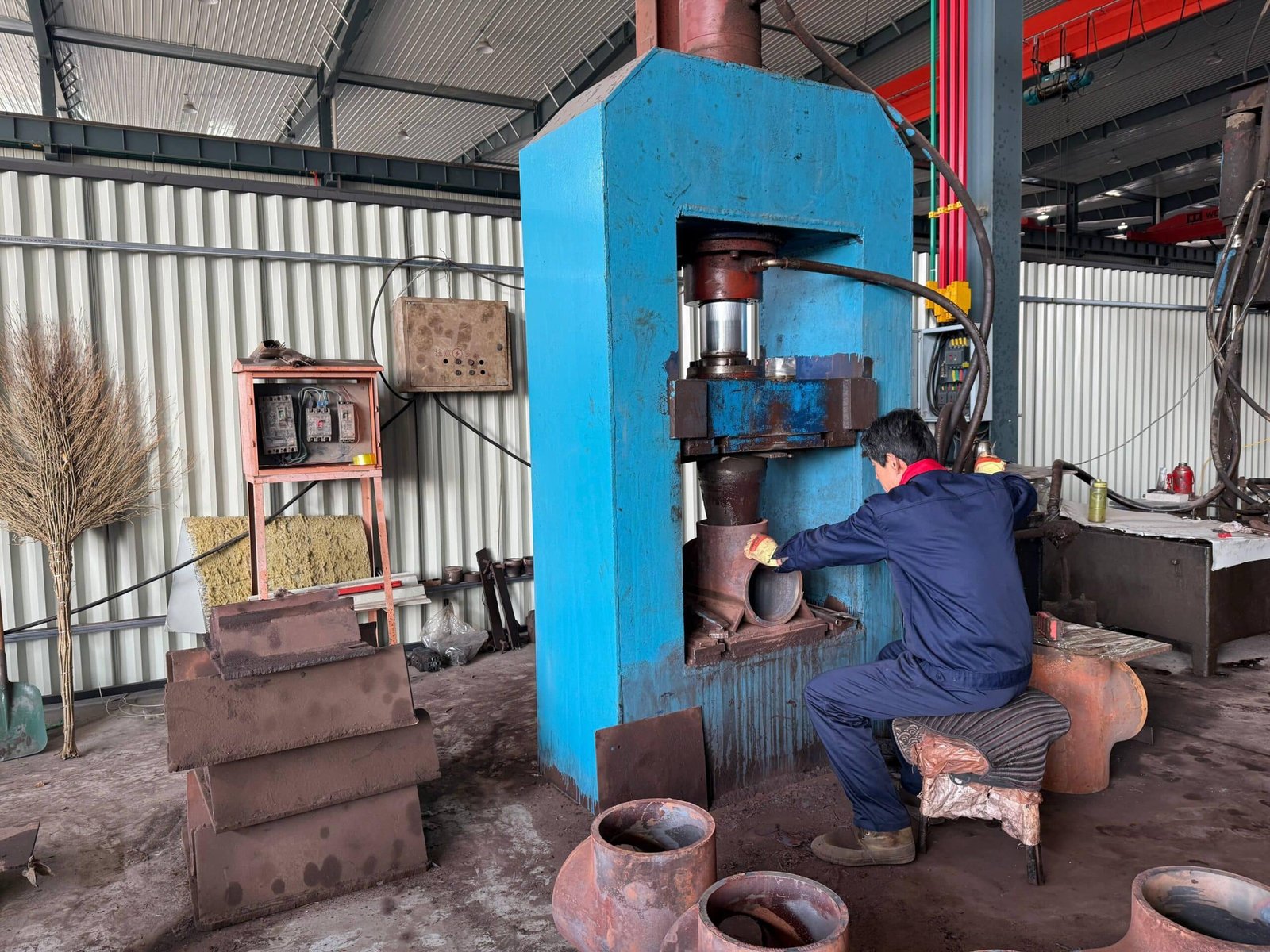
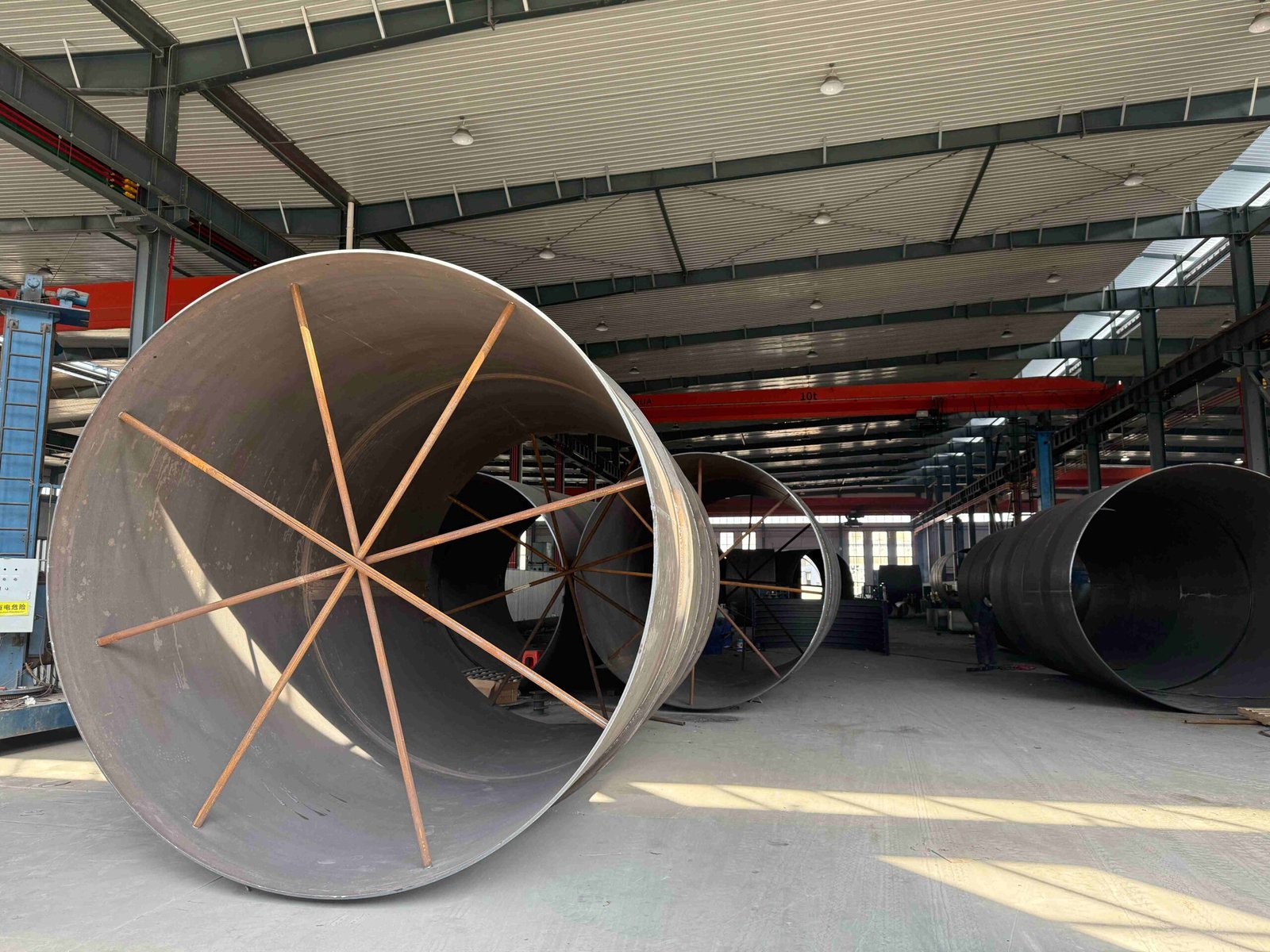
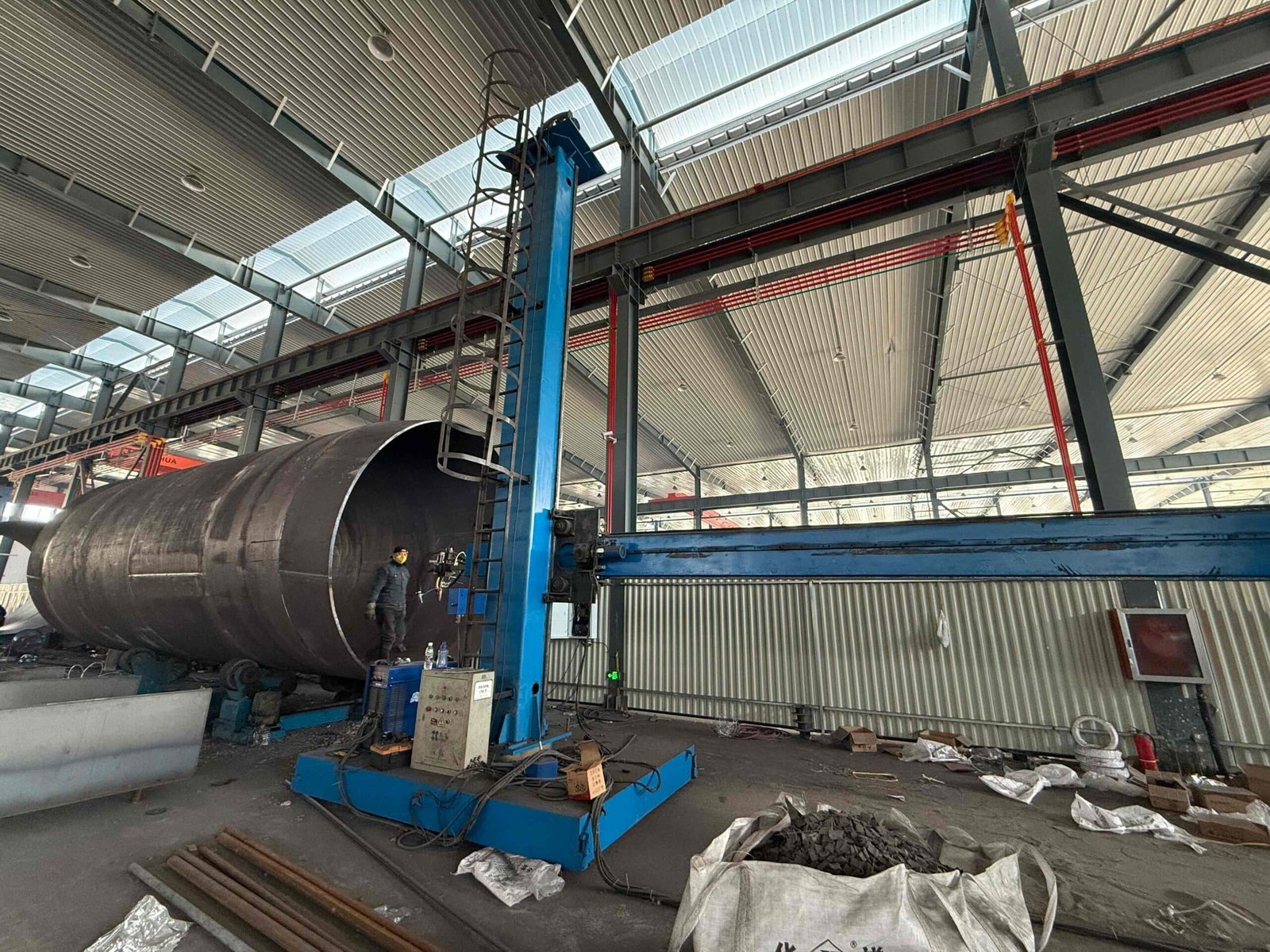
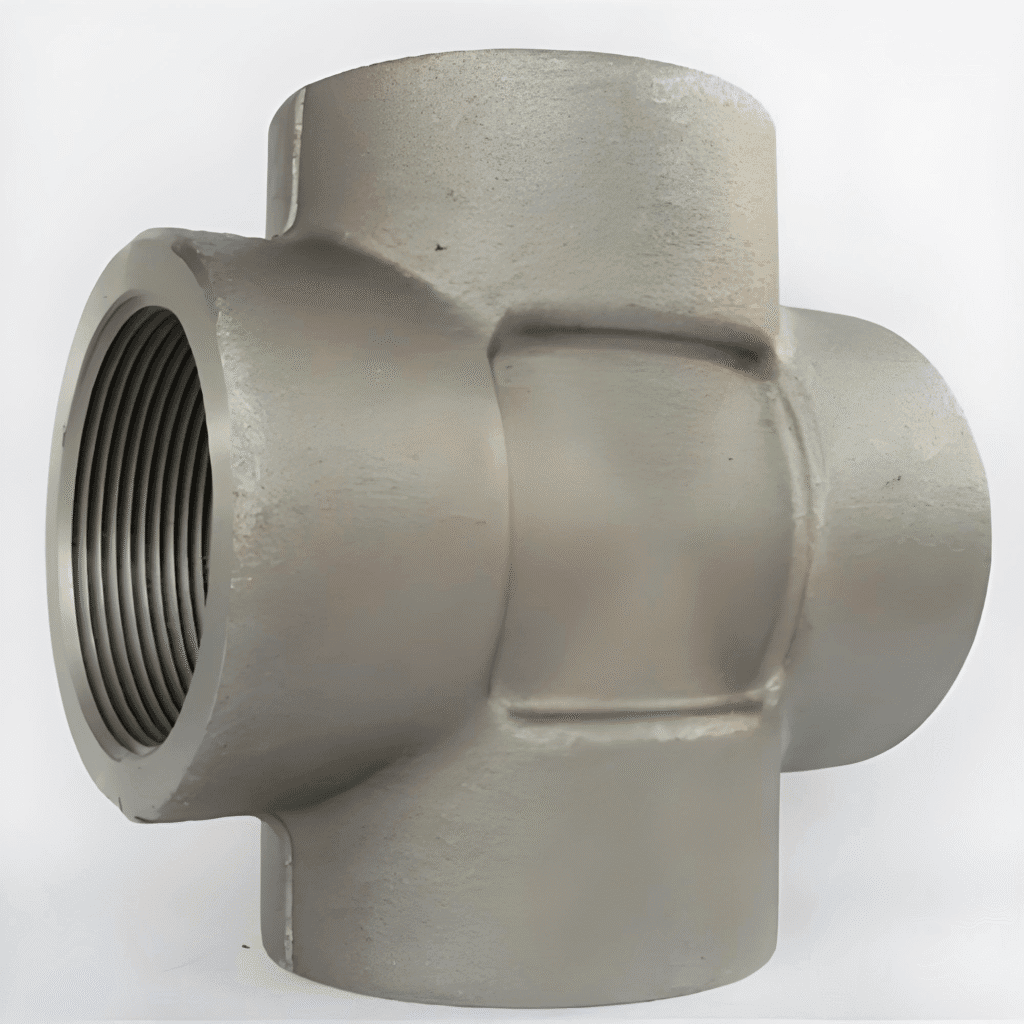
Pipe Cross
Pipe Cross could be ranged from direction angle, connection types, length and radius, material types.
Classified by Interface Dimensions
The interface dimensions of a Pipe Cross define the geometric relationship between its run and branch ports, determining flow distribution symmetry and system compatibility. Precision in diameter ratios and center-to-end distances (±1.0 mm per ASME B16.9) is critical to minimize turbulent resistance and ensure structural load balance under operational pressures
Equal Cross
The equal-diameter cross adopts a symmetrical design, and the main pipe and branch pipe interfaces maintain the same nominal size (such as DN100×DN100), ensuring uniform flow/confluence of the fluid and eliminating turbulence and pressure loss caused by sudden changes in pipe diameter. Its Center-to-End accuracy is controlled at ±1.0 mm.
The equal-diameter cross has good compatibility and can seamlessly connect to ASME/EN/DIN piping systems. The standard sizes include NPS 1/2″~48″. At the same time, its symmetrical structure can reduce vortexes and increase the life of pumps and valves.
Reducing Cross
The branch pipe diameter of the reducing cross is smaller than the main pipe (such as DN150×DN100), and flow regulation and pressure control are achieved through gradual change of pipe diameter. The center lines of the main pipe and the branch pipe are orthogonal, and the branch flow rate ratio must be ≤1.5 (API 14E anti-erosion specification), which is suitable for industrial scenarios that require energy recovery or throttling.
Classified by Connection Types
Connection methodology dictates installation efficiency and seal reliability. Butt-welded joints achieve 1000-bar containment through full-penetration welds (per ASME B16.25 bevel specs), while quick-connect systems (e.g., PZA-type clamps) enable tool-free maintenance in low-pressure sanitary applications—critical for hygienic industries requiring frequent disassembly
Classified by Material
Material composition governs corrosion resistance, pressure-temperature limits, and fluid compatibility. Industry-grade Crosses must adhere to ASTM/ASME material standards (e.g., A403 for stainless steel) to prevent degradation in aggressive media—such as H₂S in oil/gas or chlorides in marine environments—while maintaining weld integrity up to 538°C
Stainless Steel Pipe Cross
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel cross pipe fittings have good corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance, so they are suitable for chemical, food processing, petroleum and other industries. Its corrosion resistance makes it particularly outstanding in marine environments.
| Subtype | Standard & Grade | Key Advantages | Application Directions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Austenitic | ASTM A403 WP304/L | • 18% Cr-8% Ni composition | • Food processing pipelines (sanitary requirements) |
| • Cost-effective corrosion resistance | • Architectural water features (SCH10S thin-wall) | ||
| • Easy fabrication | • Weak acid chemical transport (pH 3-6) | ||
| Austenitic (Mo-Added) | ASTM A403 WP316/L | • 2-3% Mo addition | • Seawater cooling systems (power plants) |
| • Superior chloride resistance | • Pharmaceutical bioreactors (electropolished) | ||
| • Non-magnetic properties | • Coastal chemical plants | ||
| Duplex | ASTM A815 S31803 (2205) | • 22% Cr-5% Ni-3% Mo | • Subsea pipeline tie-ins |
| • 2x strength of 304SS | • Sour gas processing (H₂S >50ppm) | ||
| • Stress corrosion cracking resistance | • Desalination plant high-pressure lines | ||
| Super Duplex | ASTM A815 S32750 (2507) | • 25% Cr-7% Ni-4% Mo | • FGD scrubber circulation loops |
| • PREN ≥42 | • Offshore topside piping | ||
| • Extreme pitting/erosion resistance | • Geothermal brine systems (high chloride) |
Carbon Steel Pipe Cross
Carbon Steel: Carbon steel cross fittings are widely used in environments that need to withstand high pressure and temperature. They are commonly used in oil and gas pipelines, industrial pipelines and other fields. Carbon steel has high strength and toughness, but poor corrosion resistance, so it needs coating or other anti-corrosion treatment.
| Subtype | Standard & Grade | Key Advantages | Application Directions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | ASTM A234 WPB | • Cost-effective • Strong and durable • Easy to weld and fabricate | General construction Water transmission systems Oil and gas pipelines |
| Medium Carbon Steel | ASTM A106 Grade C | • Higher tensile strength • Better hardenability • Improved wear resistance | • Heavy machinery • Automotive applications • Pressure vessel fabrication |
| High Carbon Steel | ASTM A333 Grade 6 | • Exceptional hardness • Excellent wear resistance • Good for high-stress environments | • Mining equipment • Tool manufacturing • Structural components |
Alloy Steel Pipe Cross
Alloy Steel: Alloy steel cross fittings are made by adding alloying elements (such as chromium, molybdenum, etc.) to increase the hardness and strength of steel. This material is suitable for environments that need to withstand extreme mechanical loads and temperature changes.
| Subtype | Standard & Grade | Key Advantages | Application Directions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chrome Molybdenum | ASTM A335 P11, P22 | • High temperature strength • Superior hardness • Enhanced corrosion resistance | • Power plants • High-temperature piping systems • Petrochemical plants |
| Nickel Alloy Steel | ASTM A213 T91 | • Excellent oxidation resistance • High strength at elevated temperatures • Good for pressure environments | • Heat exchangers • High-pressure steam systems • Chemical processing industries |
| Manganese Steel | ASTM A128 Grade B | • High impact and abrasion resistance • Excellent wear resistance | • Mining machinery • Crusher parts • Rail tracks |
Material Selection Guide
| Criteria | Carbon Steel | Alloy Steel | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance Requirements | – High tensile strength – Cost-effective for high-volume applications – Easy fabrication and welding | – Excellent mechanical properties for high temperature & pressure – Suitable for high-stress and high-load conditions – Better hardness and toughness than Carbon Steel | – Outstanding corrosion resistance – High resistance to rust, oxidation, and acidic conditions – Suitable for food, marine, and chemical industries |
| Applications | – Oil & gas pipelines – Water transmission systems – Industrial piping | – Power plant piping (high heat) – Steam boilers, pressure vessels – Mechanical parts for high-stress environments | – Food and beverage pipelines – Pharmaceutical equipment – Marine and offshore applications |
| Environmental Conditions | – Vulnerable to rust and corrosion in wet environments – Usually coated to prevent corrosion – Works well in low to moderate temperature ranges | – Corrosion-resistant with protective coatings, better than Carbon Steel – Suitable for exposure to moderate chemicals – Can be used in high-pressure systems with proper treatment | – Excellent corrosion resistance (e.g., chloride environments, seawater) – Ideal for marine, coastal, and food-grade applications – Resists rust in coastal and harsh chemical environments |
| Cost Considerations | – Most cost-effective material for construction and infrastructure – Economical for large-scale production | – Higher cost due to alloying elements like chromium, molybdenum, etc. – Higher material cost but provides long-term durability in high-demand environments | – More expensive than Carbon Steel, but provides better longevity and resistance – Long-lasting and durable, reducing long-term maintenance costs |
| Fabrication & Installation | – Easy to weld and machine – Commonly available and simple to install | – Requires precise welding, heat treatment, and special techniques – More complex welding due to alloying elements | – Easier to fabricate than Alloy Steel but requires attention to welding – Requires specific equipment for welding (e.g., argon welding for some grades) |
| Specific Applications | – Water pipes – Structural supports for buildings, bridges, and factories – Industrial machinery & equipment | – Pressure vessels, heat exchangers – Marine equipment, gas turbines – Oil & gas rigs, high-stress pipelines | – Chemical reactors, pharmaceutical systems – Heat exchangers, food production lines – Pharmaceutical equipment |
| Standards & Grades | – ASTM A234 WPB, A106 Grade C – Widely used for general piping, flanges, and fittings | – ASTM A335 P11, A213 T91, A234 – Common for high-pressure and high-temperature piping | – ASTM A403 WP304/L, WP316/L, ASTM A312 – Standard for general-purpose and sanitary piping systems |
| Key Advantages | – Low cost and high availability – Suitable for high-volume applications – Good weldability and easy fabrication | – Superior mechanical properties and higher resistance to heat and pressure – Longer service life in high-temperature environments | – Excellent corrosion and oxidation resistance – Ideal for food-grade, sanitary, and chemical processing systems |
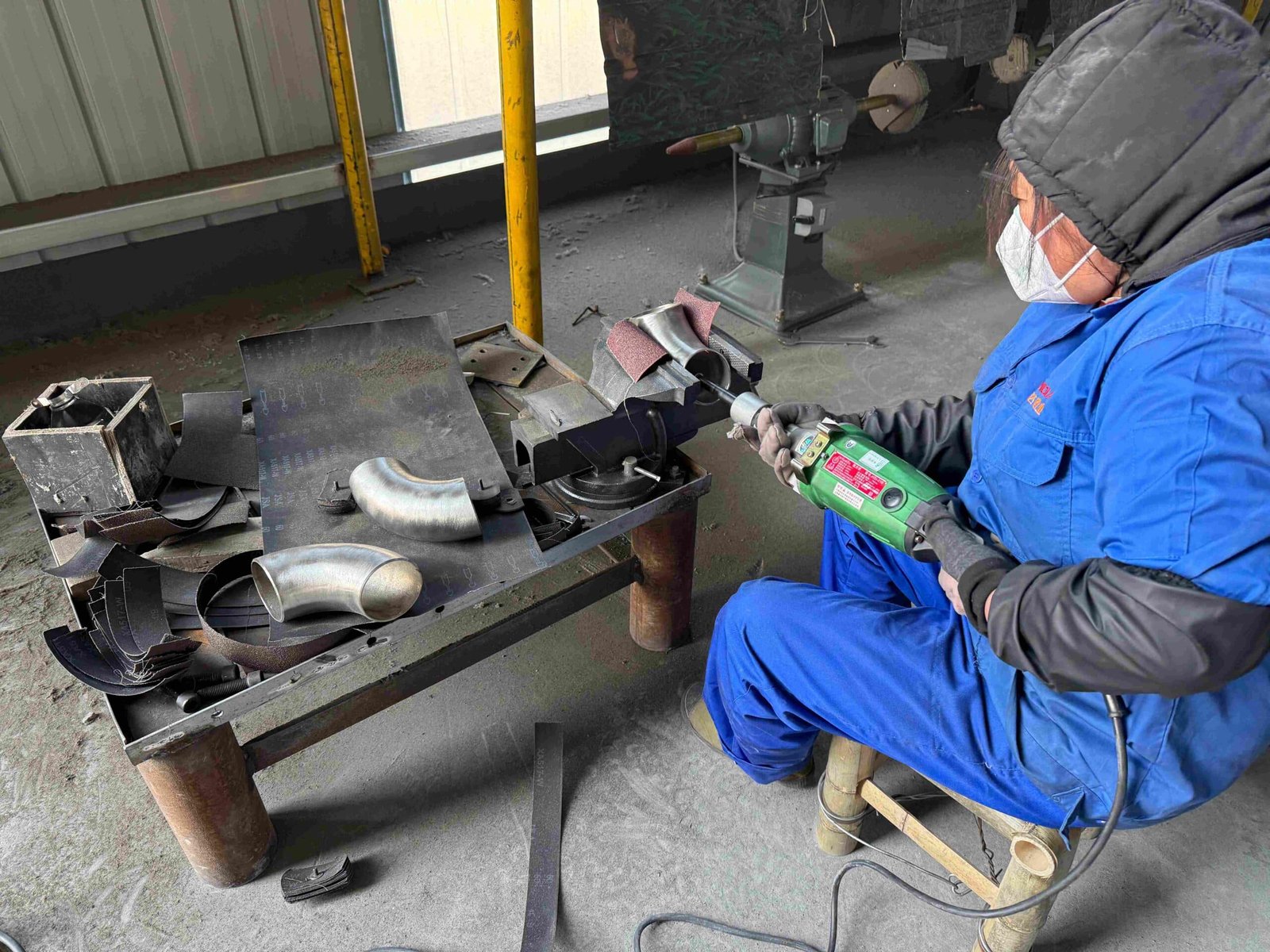
Customized Pipe Cross Process
The following options are for you to customize. If you don’t have a design drawing, you can also consult our engineers and let us help you draw it.
size
Specified pipeline size, including pipe elbow direction angle, thickness, bolt hole diameter, bolt hole distance, etc.
Material
Using specified material suitable for pipeline engineering according to your requirements.
Shape
can be customized with pipe elbow such as Reducing Elbow.
Connection
Butt Weld Elbows, Socket Weld Elbows, Threaded Elbows, etc., which can be selected.
Special Treatment
Special treatments such as surface coatings and anti-corrosion can be made according to your needs.
The customization process for Pipe Elbow is generally as follows:
requirements
Confirmation
Communicate in detail to determine the requirements for pipe elbow size, material, pressure, connection method, etc.
Raw Material Preparation
Cut pipe to dimensions on process card using CNC cutting machines (±1mm tolerance). Remove burrs, scale, and debris from cut ends. Grind pipe ends smooth.
Billet Pre-Treatment
Spray internal coating lead powder graphite binder solution 0.2-0.3mm thickness dry in 120C oven for two hours
Hot Push Bending
Install mandrel die heat tube via medium-frequency induction to 750±10C hydraulic push at 50-80mms with 300-500t force
Post Forming Processing
Cool via air mist mixture control 50-80Cmin rate lathe machine ends ensure wall uniformity bevel 375±25deg
Quality Inspection
Check surface defects verify dimensions with calibrated gauges perform 100 percent MT and UT nondestructive testing
Surface Treatment
Shot blast using cast steel shot achieve SA25 cleanliness apply epoxy primer and polyurethane topcoat at specified thickness
Packaging Storage
Protect ends with plastic caps separate elbows with foam spacers include certificates store in dry ventilated warehouse
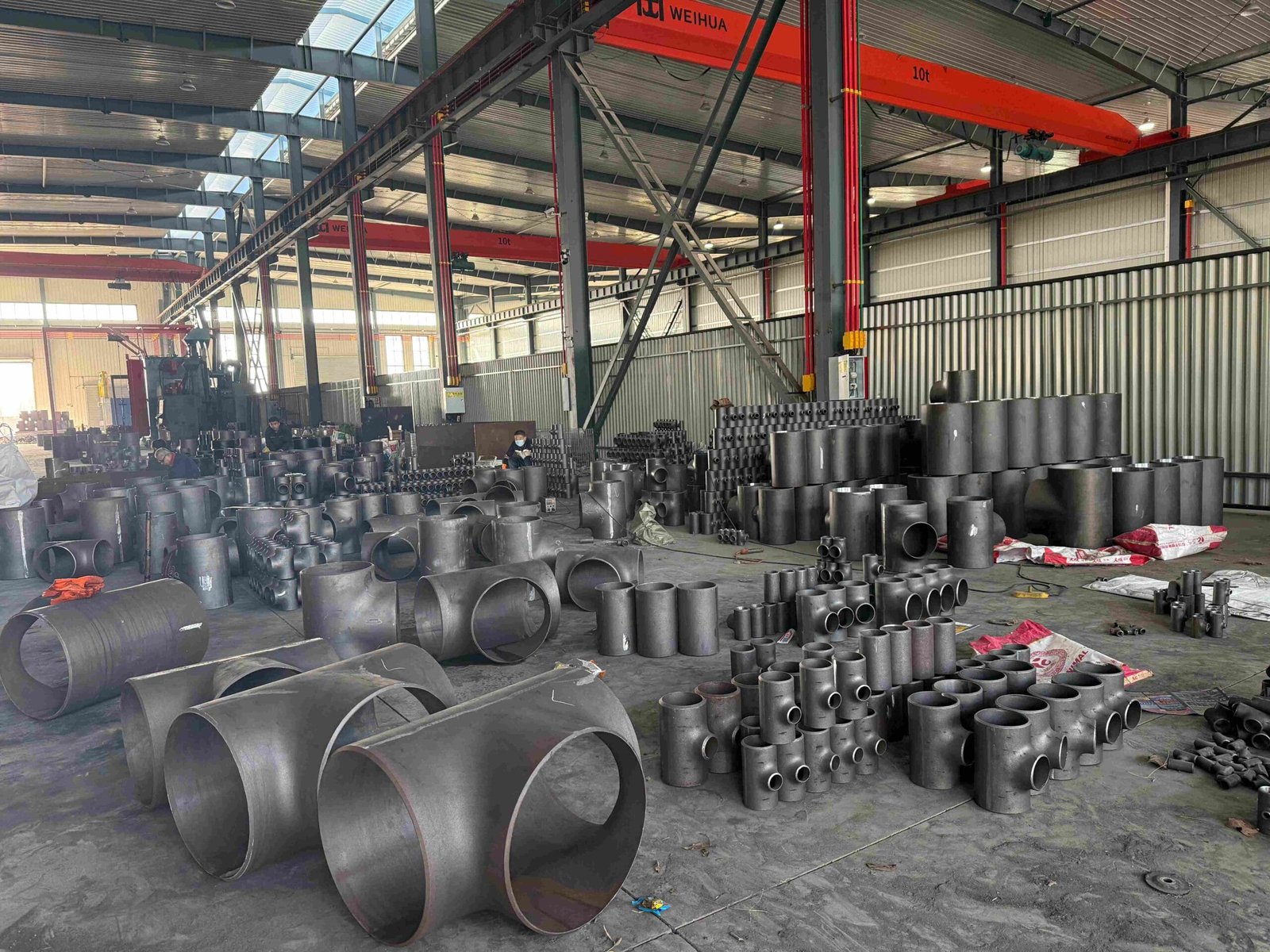
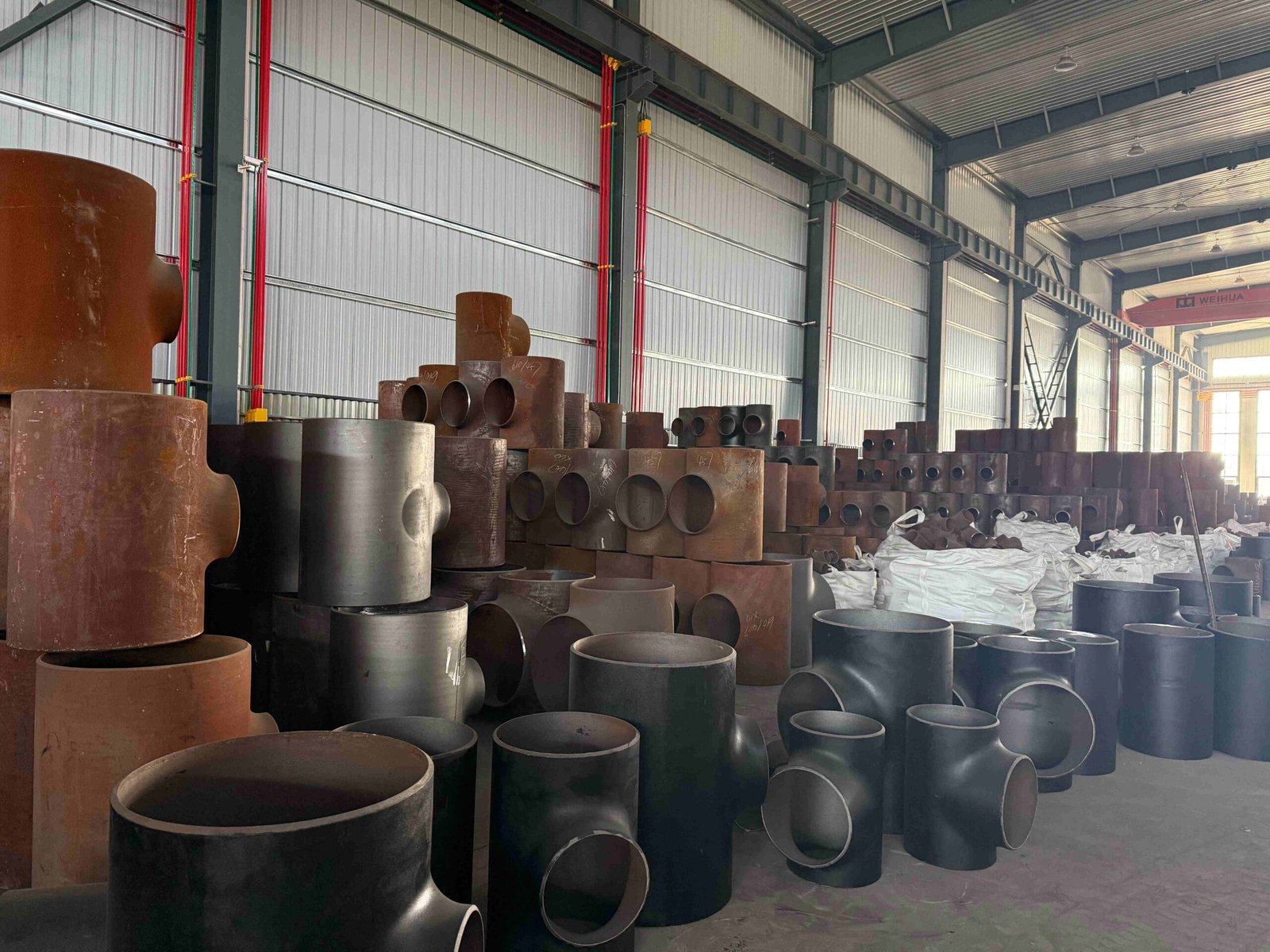
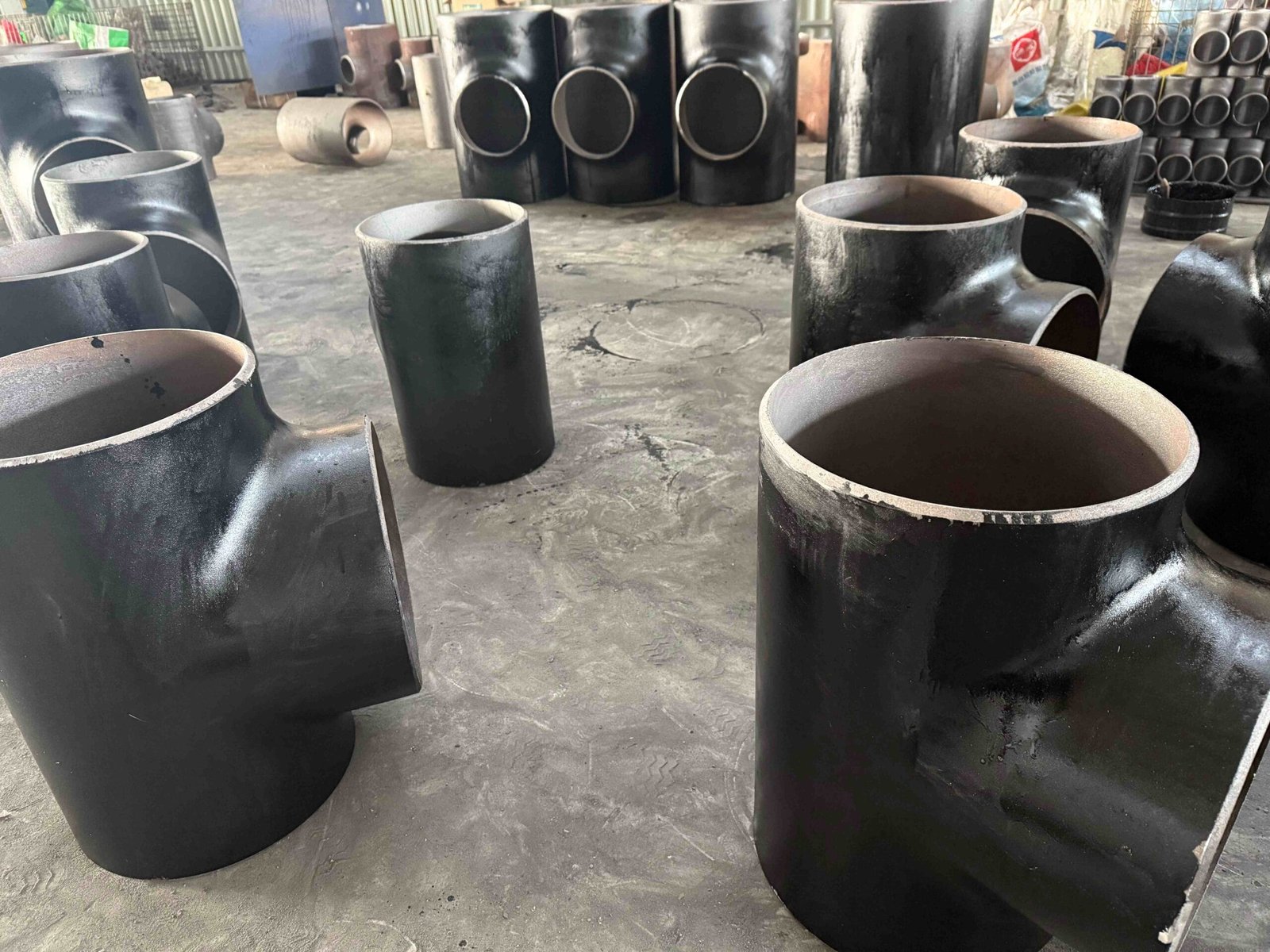
Image Gallery
Here are various Pipe Cross produced by YANHAO. You can click on the pictures to enlarge them. As a company with 25 years of Pipe Cross production experience, YANHAO supports all types of Pipe Cross production.
Pipe Cross Image Gallery
FAQs About Pipe Cross
About YANHAO

YANHAO is a China Flange Manufacturer located in Hebei Province, China. It is one of the few professional Flange suppliers in China.
We have many years of experience in flange production and have multiple flange production lines. We have sufficient stock of raw materials, rich inventory, fast delivery, and can ship within three days. At the same time, the price is affordable. You are welcome to consult and purchase!
In addition, we can provide a variety of customized flanges and pipe fittings. Customers can give drawings or samples, and our company will produce them to fit your specific requirements.
Our company was founded in 2000 and has more than 300+ employees, including 85+ middle and senior engineering and technical personnel. Our company has several production lines and covers an area of 150,000 square meters and a building area of 30,000 square meters.
300+
Number Of Workers
85+
Mid&Senior Engineers
150,000
Square Meters of Area
25+
Years of Experience
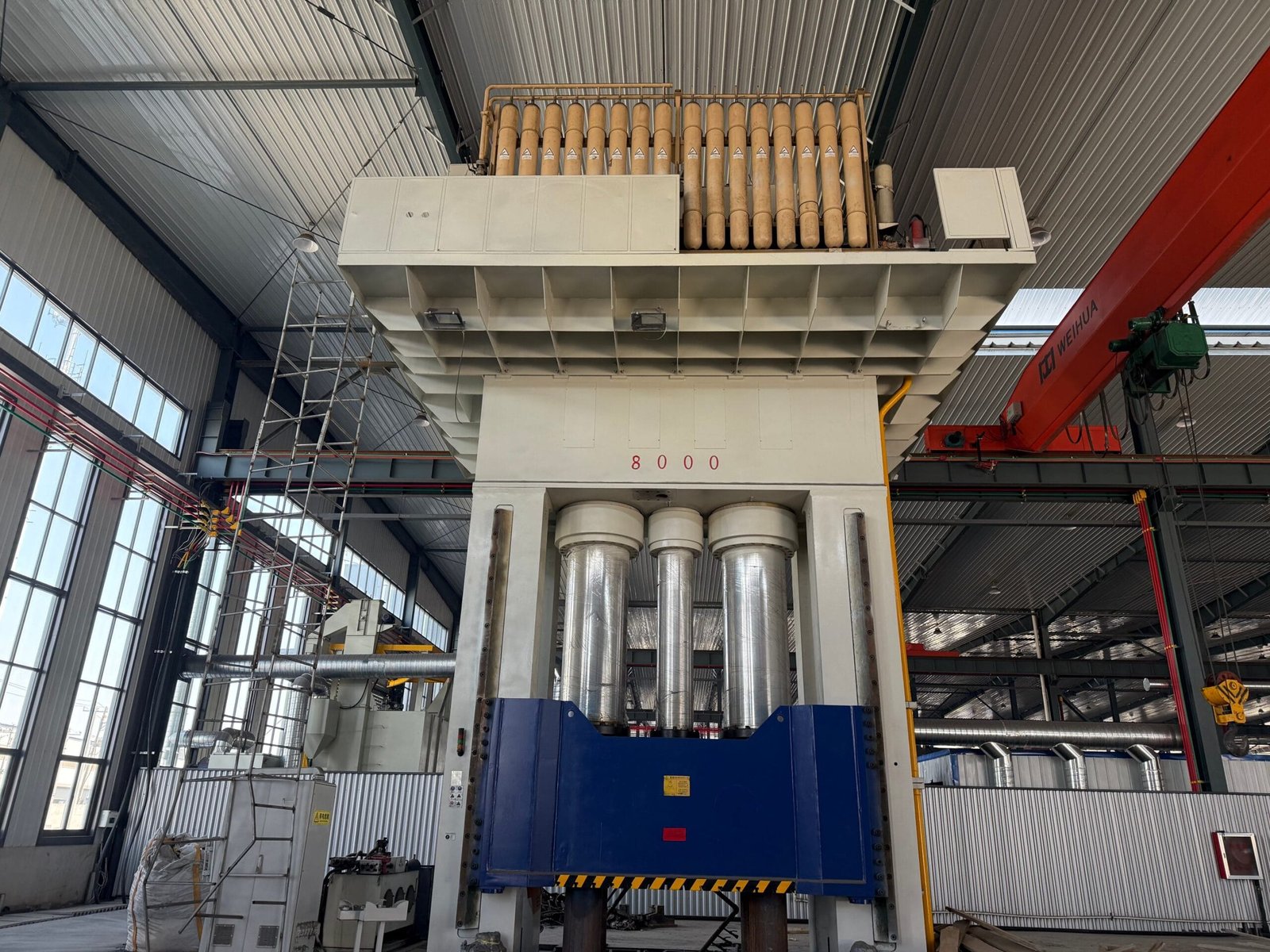
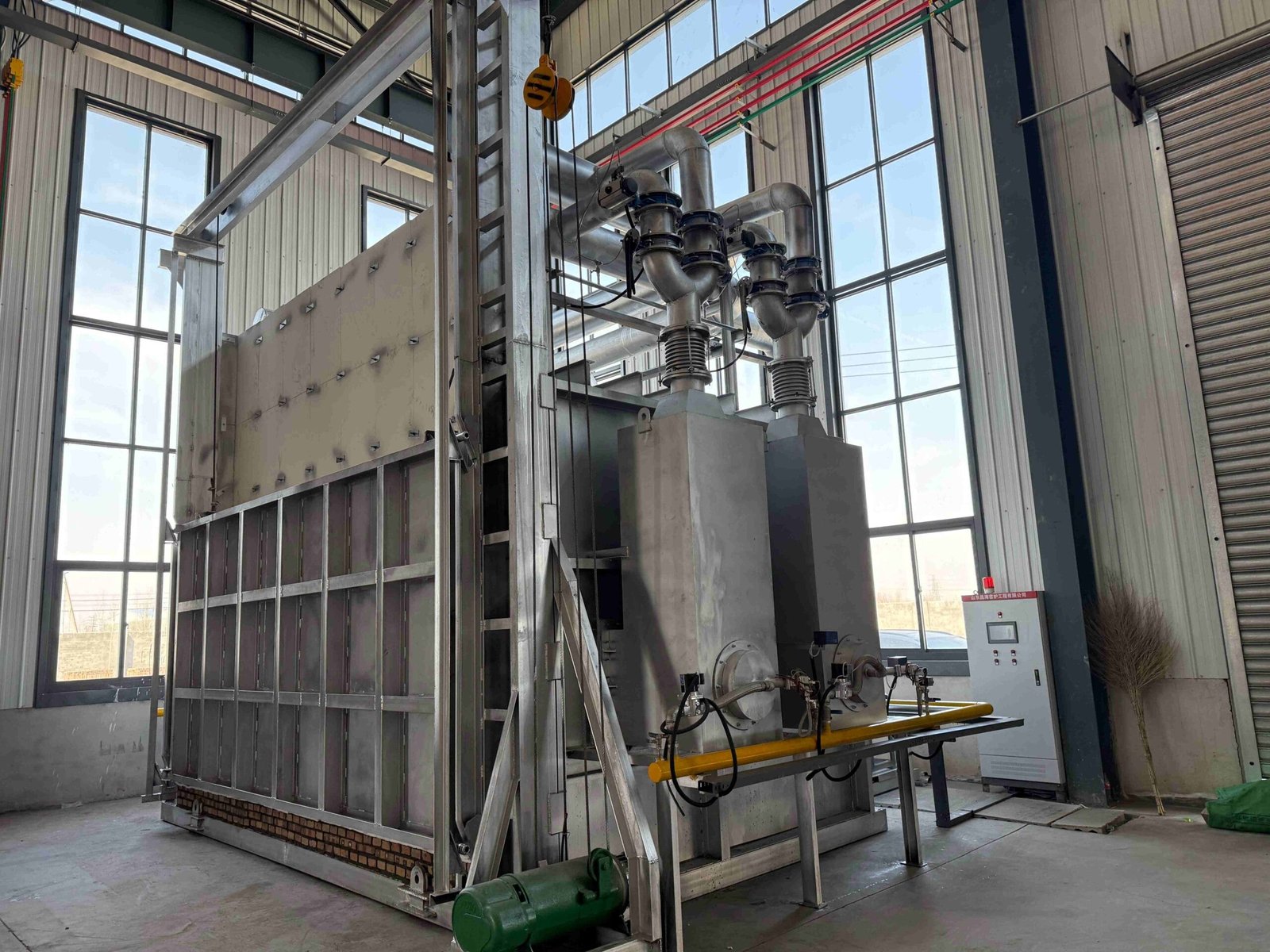
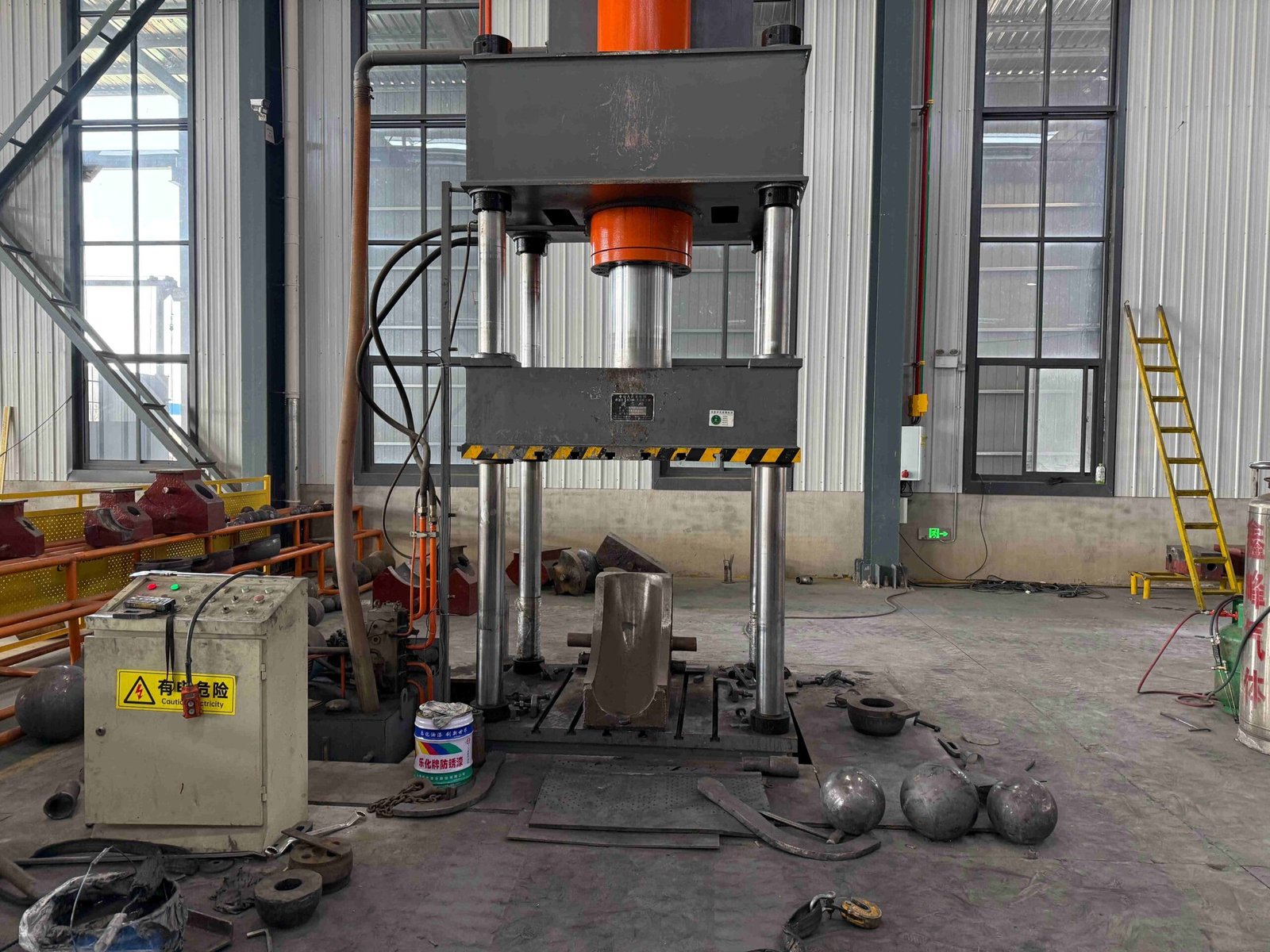
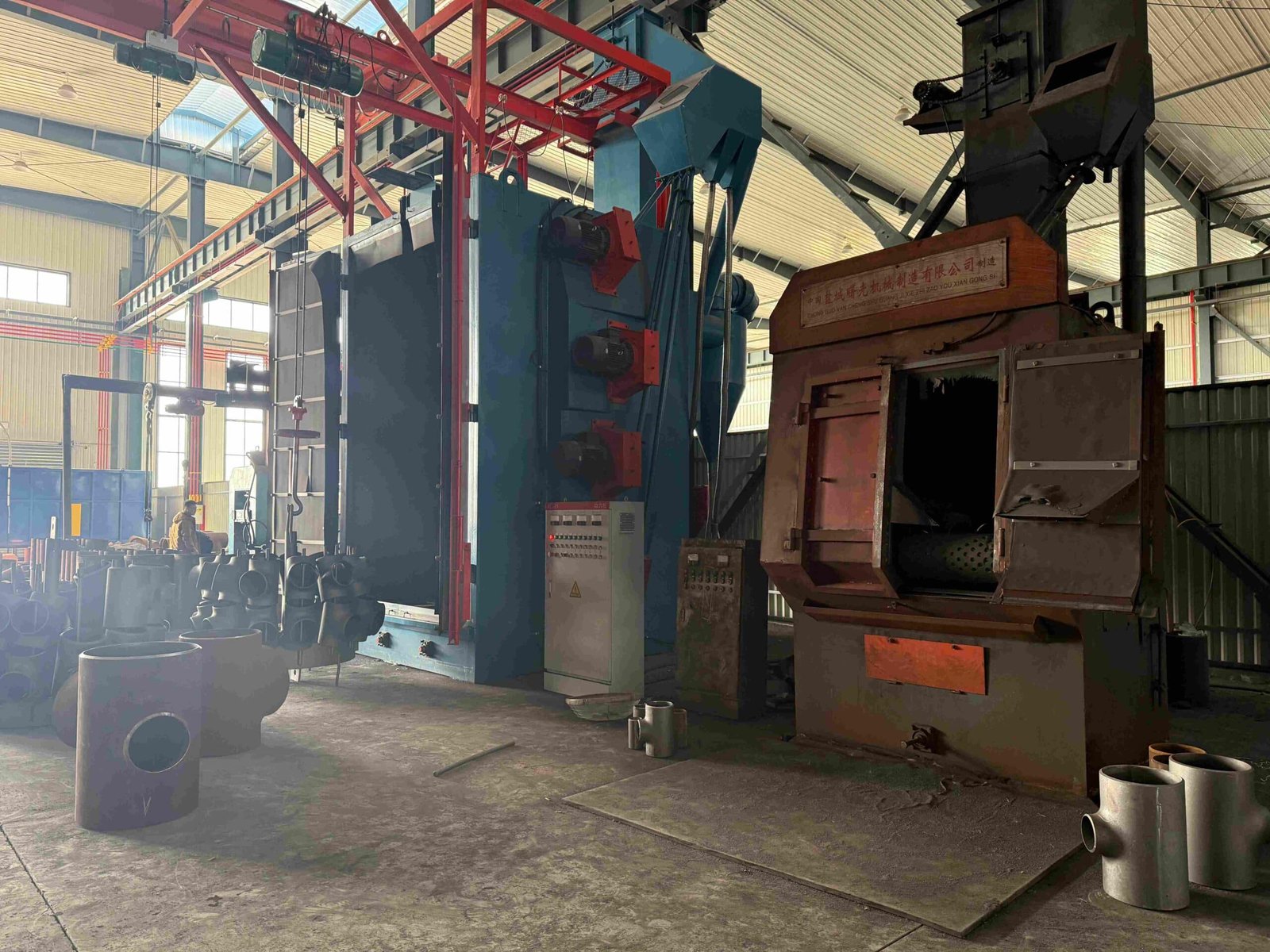
Our Production Line
Our company has 8 pipe fitting production lines and 5 flange production lines. It has a full set of medium-frequency elbow hot-pushing machines, hot-die presses for reducers, cold-extrusion hydraulic presses for tees, forging hammers, vertical lathes, drilling machines, and other process-forming and mechanical processing equipment.
Among them, the Φ1020 mm large-diameter medium-frequency hydraulic pushing machine, Φ1420 mm large-diameter medium-frequency bending machine, and Φ2438 mm 4,000-ton large hot-die press have an annual production capacity of more than 80,000 tons.
8
Pipe Fitting Production Lines
5
Flange Production Lines
80,000 tons
Annual Production Capacity
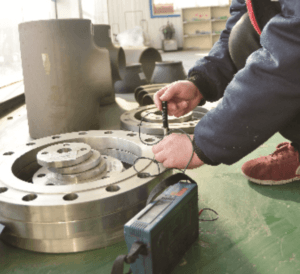
Quality Testing & Certificates
Our company is also equipped with a full set of physical and chemical testing, including spectrometer direct reading, non-destructive testing, heat treatment, water pressure testing, and other product quality testing equipment, providing a reliable guarantee for the production of high-quality products.