How to Customize a Non-standard Large Flange
In industrial production, large-diameter non-standard flanges have a wide range of applications, from petrochemicals to power energy, covering almost all fields requiring pipeline connections.However, standard flanges often cannot meet the needs of special operating conditions, making custom-made non-standard flanges a necessity.
This article will introduce the specific steps for customizing large-diameter non-standard flanges:
Step 1: Material Selection
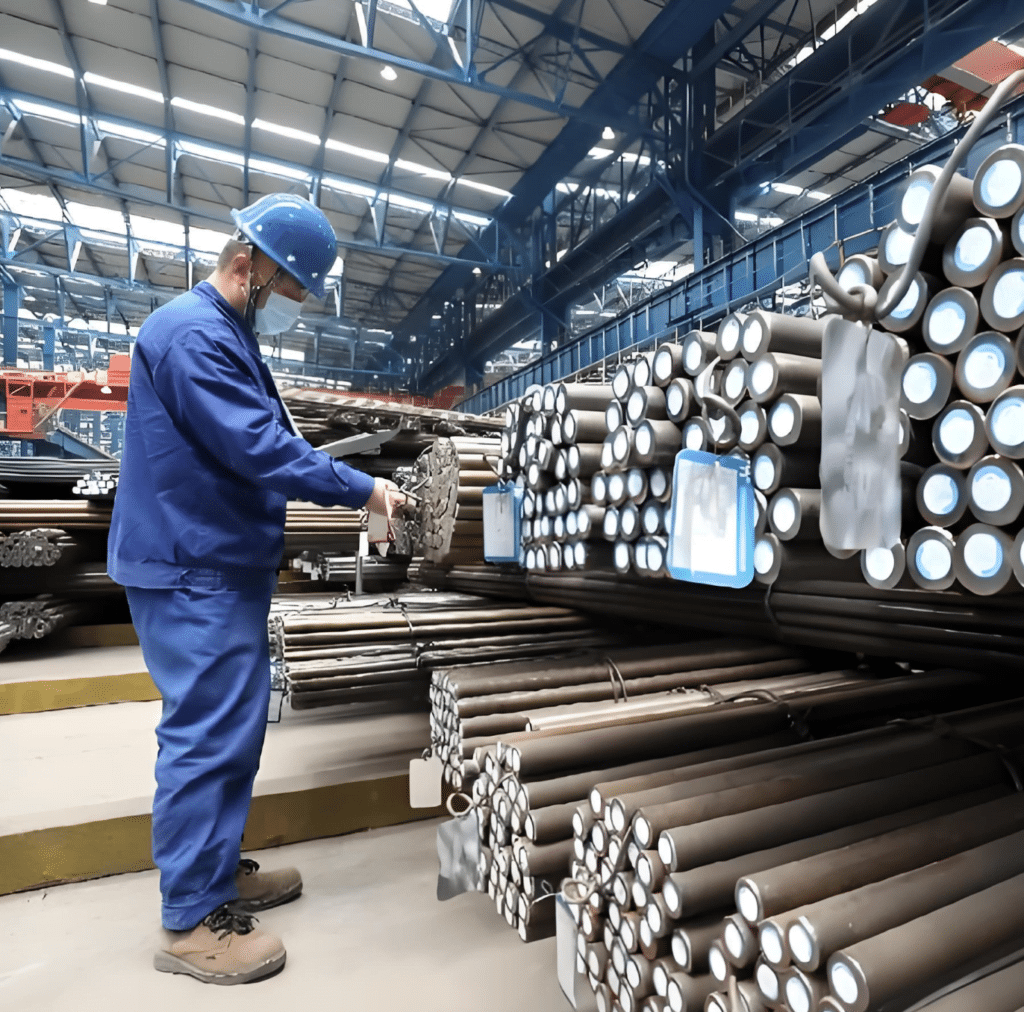

The Material choice depends on the specific application scenario.
Many people believe that stainless steel flanges are all that’s needed, but different operating conditions require significantly different materials.
For example, in coastal areas, 316L stainless steel offers significantly better corrosion resistance than 304; while under high temperature and pressure, SA105 carbon steel flanges exhibit superior stability.
A real-world example: A chemical plant company purchased a batch of standard 304 flanges for transporting acidic media, only to experience severe pitting corrosion after six months. After switching to custom-made 2205 double-sided stainless steel flanges, their service life increased threefold.
It’s crucial to note that the material thickness of non-standard flanges typically needs to be 10%-15% greater than standard flanges, especially for large-diameter products above DN600 (Pipe flange size chart >>) .
If you require custom-made non-standard flanges, especially large ones, please communicate with our engineering team in advance. We will provide you with the most suitable materials.
Step 2: Flange structural design
It needs to consider the installation Process.
The biggest taboo in non-standard customization is designing in isolation. We’ve encountered many cases where the design drawings were excellent, but the flanges simply couldn’t be installed on-site. We recommend paying attention to three details in the design:
A tip: When the flange diameter exceeds DN800 (Pipe flange size chart >>), a split-type structural design is highly recommended. This reduces transportation difficulties and the risk of welding deformation.
Therefore, when designing non-standard flanges, you need to provide the following important parameters:
If you are unsure of the specific parameters, you can also describe your usage scenario in detail via email, along with your pipe fitting parameters, and we will design and match them for you.
During the design process, our engineers comprehensively consider factors such as the flange’s structural strength, sealing performance, and ease of installation. Structural strength ensures the flange will not deform or break under the predetermined pressure. Sealing performance guarantees no leakage at pipe connections. Ease of installation relates to the ease of on-site construction.
The drafting stage requires the creation of detailed engineering drawings, including assembly drawings and component drawings. All dimensions, tolerances, surface treatment requirements, and other special specifications will be clearly marked on the drawings.
Step 3: The manufacturing process of flanges
The manufacturing process of non-standard flanges varies depending on the materials and production volume.
Common manufacturing methods include forging, casting, and machining.
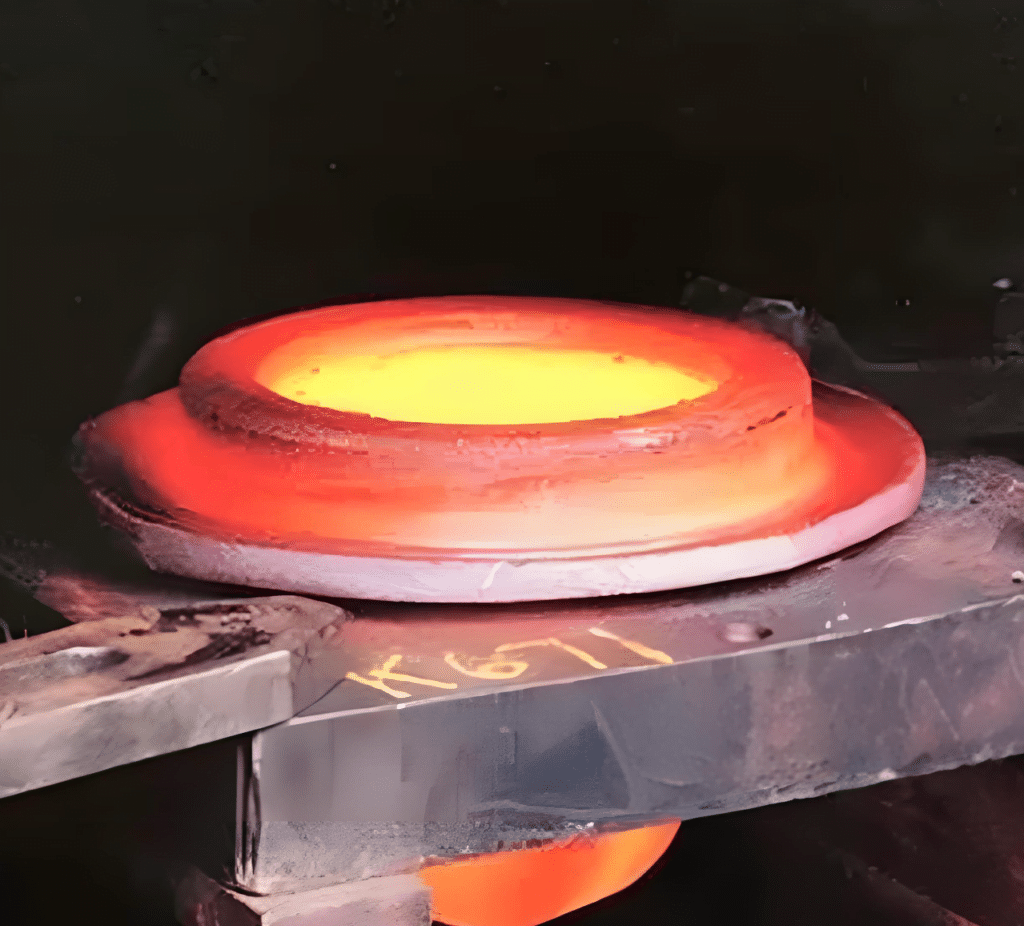

During the manufacturing process, strict quality control is required at every step. From blanking, heating, forming to heat treatment, each step can affect the quality of the final product. The heat treatment process, in particular, has a decisive impact on the mechanical properties of the flange and must be strictly implemented according to process specifications.
The main challenges in machining large-diameter non-standard flanges lie in three aspects:
Read more: How a Flange Is Made: The Flange Production/Manufacturing Process
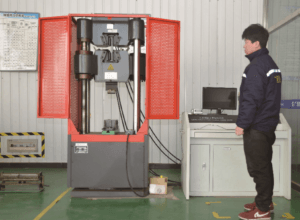
Step 4: Quality Control
We conduct a complete quality inspection before delivery to the customer.
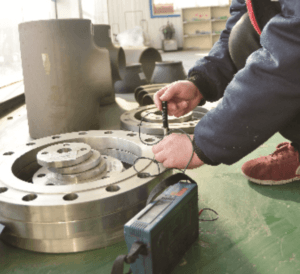
Quality inspection is a crucial step in ensuring that non-standard flanges meet requirements. Inspection includes dimensional checks, material verification, and performance testing.
Dimensional checks verify that the finished flange’s geometric dimensions match the drawings. This includes basic dimensions such as outer diameter, inner diameter, and thickness, as well as detailed dimensions such as bolt hole locations and sealing surface shapes. Material verification involves chemical composition analysis and mechanical performance testing to confirm that the materials used meet requirements.
Performance testing may include pressure testing and non-destructive testing, depending on the application requirements. Pressure testing simulates working conditions to test the flange’s pressure-bearing capacity. Non-destructive testing uses methods such as ultrasonic testing and X-rays to inspect for internal defects.
Only flanges that pass inspection are delivered to the user. Non-conforming products discovered during inspection are reworked or scrapped in various ways to ensure that all products leaving the factory meet quality standards.
Our company is equipped with a full set of physical and chemical testing, including spectrometer direct reading, non-destructive testing, heat treatment, water pressure testing, and other product quality testing equipment, providing a reliable guarantee for the production of high-quality products.
Finally
There are a few points to consider when ordering custom flanges for engineering projects. Choosing an experienced manufacturer is crucial. Professional manufacturers not only possess advanced production equipment but also have a rigorous quality management system, enabling them to provide reliable products.
Users should clearly define their budget; custom flanges typically cost more than standard products, but through proper design and material selection, costs can be controlled while ensuring quality. Users need to understand relevant standards and specifications to ensure that the custom flanges meet project requirements and avoid safety hazards caused by improper design.
Author: Lewis Liu
Hello, my name is Lewis Liu, and I’m a professional sales engineer with over a decade of expertise in the flange fittings sector.
I am quite informed about flange selection, installation, and maintenance. I am passionate about providing customers with the greatest solutions for keeping their pipeline systems running smoothly, safely, and dependably.
If you have any queries or concerns concerning flange fittings for your pipelines, whether they are about selection, material choice, specification requirements, or anything else, please contact me at any time. I am dedicated to providing expert advice and assistance to help you make educated decisions and reach your objectives.